Overview
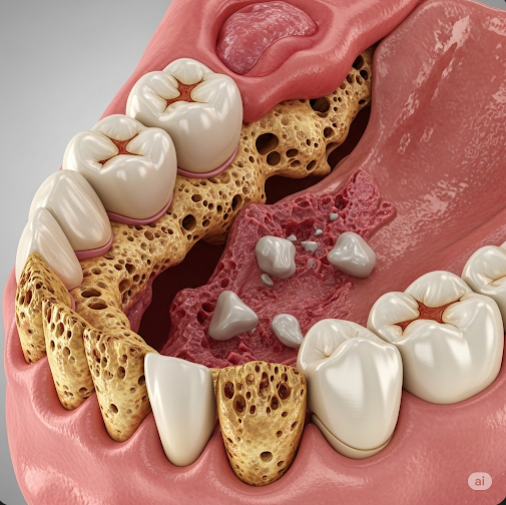
Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (ONJ) is a severe bone disease characterized by the death of jawbone tissue due to reduced blood flow. It often occurs in patients receiving certain medications, such as bisphosphonates or denosumab, commonly used to treat osteoporosis or metastatic cancers. ONJ can lead to pain, infection, and exposed bone in the mouth. In Korea, specialized dental and maxillofacial centers provide advanced diagnosis and multidisciplinary treatment options to manage ONJ effectively.
What is Osteonecrosis of the Jaw?
ONJ occurs when the blood supply to the jawbone is compromised, leading to bone tissue death and poor healing after dental procedures or spontaneously. It is most frequently linked to the use of antiresorptive medications and sometimes radiation therapy to the head and neck. The condition is challenging to treat due to the jawbone’s constant exposure to bacteria and mechanical forces from chewing.
Symptoms
Symptoms of ONJ may include:
- Pain or swelling in the jaw or mouth
- Exposed bone visible through the gum tissue
- Loosening of teeth
- Infection or pus discharge from the affected area
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing
- Numbness or a heavy feeling in the jaw
Causes
ONJ is primarily caused by:
- Use of bisphosphonates or denosumab, especially intravenous forms
- Radiation therapy to the head and neck (osteoradionecrosis)
- Dental trauma or invasive dental procedures such as tooth extractions
- Poor oral hygiene or pre-existing dental infections
Risk Factors
Risk factors increasing ONJ likelihood include:
- High-dose or long-term use of antiresorptive drugs
- Cancer patients undergoing bone-targeted therapies
- History of radiation therapy to the jaw
- Poor dental health or periodontal disease
- Smoking and diabetes
- Invasive dental surgeries
Complications
If left untreated, ONJ can cause:
- Chronic pain and infection
- Spread of infection to adjacent tissues or bloodstream
- Difficulty eating, speaking, or maintaining oral hygiene
- Jaw fractures in severe cases
- Significant reduction in quality of life
Prevention
Prevention strategies for ONJ focus on dental care and medication management:
- Thorough dental examination and treatment before starting antiresorptive therapy
- Maintaining excellent oral hygiene
- Avoiding invasive dental procedures during treatment when possible
- Regular dental check-ups during medication use
- Prompt treatment of oral infections
Treatment Options in Korea
In Korea, ONJ treatment is multidisciplinary and tailored to disease severity:
- Conservative care: Pain control, antibiotics, oral rinses, and avoiding further trauma
- Surgical intervention: Removal of necrotic bone in advanced cases to promote healing
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy: Sometimes used to enhance tissue repair
- Medication review: Adjusting or temporarily stopping antiresorptive drugs under physician guidance
- Supportive care: Nutritional support and rehabilitation to maintain oral function
Leading Korean dental hospitals and maxillofacial surgery centers utilize advanced imaging and collaborative care teams to provide the best outcomes for patients with ONJ.