Overview
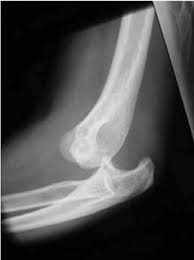
Osteochondritis Dissecans (OCD) is a joint condition where a fragment of bone and its overlying cartilage partially or completely separates from the end of a bone due to loss of blood supply. This can lead to pain, swelling, and joint dysfunction. OCD most commonly affects the knee but can also involve the ankle and elbow. In Korea, orthopedic specialists use advanced imaging and both conservative and surgical treatments to manage OCD effectively and help patients return to full activity.
What is Osteochondritis Dissecans?
OCD is a joint disorder in which a segment of bone beneath the cartilage dies from lack of blood flow (avascular necrosis), causing the bone and cartilage to crack and sometimes detach. This loose fragment can cause pain, swelling, and mechanical symptoms like catching or locking of the joint. The condition is more common in adolescents and young adults, often related to repetitive trauma or stress.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of Osteochondritis Dissecans include:
- Joint pain that worsens with activity
- Swelling and stiffness around the affected joint
- A sensation of the joint catching, locking, or giving way
- Reduced range of motion
- Tenderness over the joint
Causes
The exact cause of OCD is unclear, but several factors are believed to contribute:
- Repetitive trauma or stress to the joint
- Ischemia (reduced blood flow) to a portion of the subchondral bone
- Genetic predisposition
- Rapid growth phases during adolescence
- Joint overuse in sports or activities
Risk Factors
Factors that increase the risk of developing OCD include:
- Participation in high-impact or repetitive stress sports (e.g., basketball, soccer, gymnastics)
- Age between 10 and 20 years, especially during growth spurts
- Male gender (slightly higher incidence)
- Previous joint injury or trauma
Complications
If left untreated or severe, OCD can lead to:
- Chronic joint pain and swelling
- Loose bodies inside the joint causing mechanical symptoms
- Early onset osteoarthritis due to cartilage damage
- Reduced joint function and mobility
Prevention
While OCD cannot always be prevented, risks can be reduced by:
- Avoiding repetitive joint overuse and trauma
- Proper training techniques and protective equipment in sports
- Prompt treatment of joint injuries
- Maintaining healthy nutrition and hydration to support bone health
Treatment Options in Korea
In Korea, treatment of Osteochondritis Dissecans depends on the patient’s age, lesion size, and stability:
- Conservative treatment: Rest, activity modification, physical therapy, and pain management for stable lesions, especially in children and adolescents.
- Surgical options: Arthroscopic drilling, fixation of loose fragments, or removal of unstable fragments for more advanced cases.
- Regenerative techniques: Procedures such as microfracture or autologous chondrocyte implantation to promote cartilage repair.
- Rehabilitation: Customized physical therapy programs to restore joint function and strength.
Korean orthopedic centers provide comprehensive care using the latest imaging modalities (MRI, CT) and minimally invasive surgery to optimize patient outcomes and reduce recovery time.