Overview
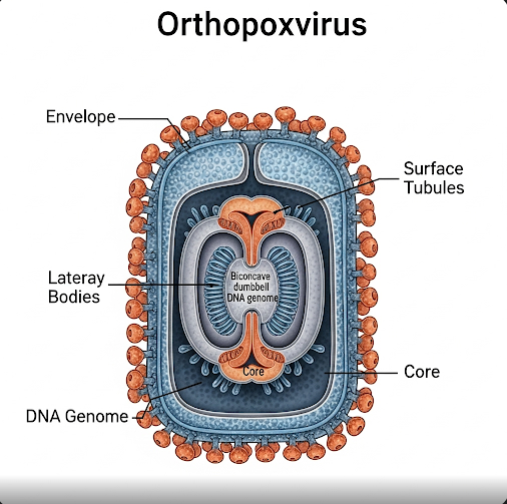
Orthopoxvirus is a genus of viruses within the Poxviridae family that includes several significant viruses affecting humans and animals. Notably, it includes the variola virus responsible for smallpox, vaccinia virus used in the smallpox vaccine, cowpox virus, and monkeypox virus. These viruses cause pox-like skin lesions and have played major roles in infectious disease history.
What is Orthopoxvirus?
Orthopoxvirus comprises large, complex DNA viruses that infect humans and various animals. The genus includes viruses that can cause diseases characterized by fever, rash, and pustular skin lesions. While smallpox has been eradicated globally, other orthopoxviruses like monkeypox continue to pose health risks, especially in certain regions.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary by virus but typically include:
- Fever and malaise
- Headache and muscle aches
- Swelling of lymph nodes
- Rash that progresses to pustules and scabs
- Lesions primarily on the face, hands, and limbs
- In severe cases, complications such as pneumonia or encephalitis
Causes
Orthopoxvirus infections result from exposure to:
- Direct contact with infected individuals or animals
- Respiratory droplets during close contact
- Contact with contaminated materials such as bedding or clothing
- Zoonotic transmission from animals like rodents or primates
Risk Factors
- Close contact with infected persons or animals
- Handling or exposure to wild or exotic animals
- Lack of vaccination against smallpox (and related viruses)
- Living in or traveling to endemic areas, particularly parts of Central and West Africa for monkeypox
- Immunocompromised individuals at higher risk for severe disease
Complications
- Secondary bacterial infections of skin lesions
- Pneumonia or respiratory complications
- Encephalitis (brain inflammation)
- Scarring and disfigurement
- In rare cases, death, especially in immunocompromised patients or young children
Prevention
- Vaccination with vaccinia-based smallpox vaccines (effective against several orthopoxviruses)
- Avoiding contact with wild animals known to carry orthopoxviruses
- Using protective equipment when caring for infected patients or animals
- Maintaining good hygiene and infection control practices
- Surveillance and prompt isolation of cases in outbreak settings
Treatment Option in Korea
South Korea has strong public health infrastructure and medical facilities prepared for orthopoxvirus infections, especially given global concerns over monkeypox outbreaks. Treatment is largely supportive and includes:
- Antiviral medications such as tecovirimat (approved for orthopoxvirus infections)
- Symptom management with analgesics and antipyretics
- Isolation and infection control to prevent spread
- Monitoring for complications in hospital settings if severe
Korean hospitals like Samsung Medical Center, Severance Hospital, and Asan Medical Center have infectious disease specialists and advanced laboratories capable of diagnosing orthopoxvirus infections. Korea also participates in international disease surveillance and vaccination programs.