Overview
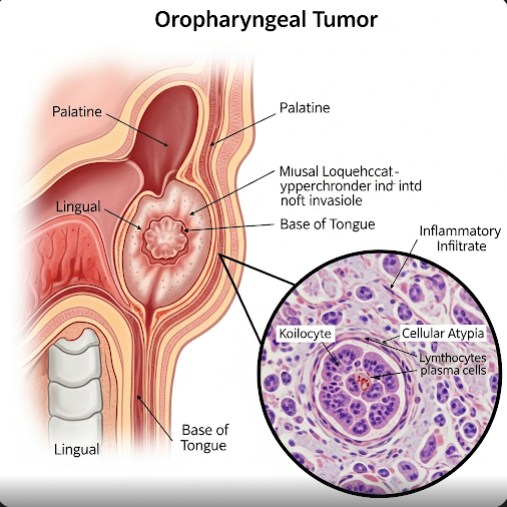
Oropharyngeal Human Papillomavirus (HPV) infection is a viral infection affecting the oropharynx, the middle part of the throat including the tonsils and base of the tongue. Certain high-risk types of HPV, especially HPV-16, are linked to the development of oropharyngeal cancers. HPV infection is now recognized as a major cause of throat cancers, particularly among younger adults. Early detection and prevention are crucial to reduce the burden of HPV-related oropharyngeal disease.
What is Oropharyngeal HPV Infection?
Oropharyngeal HPV infection occurs when the human papillomavirus infects the mucosal cells lining the oropharynx. Most HPV infections are cleared by the immune system without symptoms, but persistent infection with high-risk HPV types can cause cellular changes that may lead to cancer. Transmission mainly occurs through oral sexual contact. Unlike cervical HPV infection, oropharyngeal HPV often remains asymptomatic until cancer develops.
Symptoms
Most people with oropharyngeal HPV infection do not show symptoms. However, persistent infection that progresses to cancer may present with:
- Persistent sore throat or discomfort
- Lump or swelling in the neck (enlarged lymph nodes)
- Difficulty swallowing or painful swallowing
- Changes in voice or hoarseness
- Ear pain without infection
- White or red patches in the throat or mouth
- Unexplained weight loss
Causes
- Infection with high-risk HPV types, especially HPV-16
- Oral sexual contact with an infected partner
- Multiple sexual partners increasing exposure risk
- Tobacco and alcohol use may increase susceptibility
- Weakened immune system
Risk Factors
- Engaging in oral sex with multiple partners
- Early age of first sexual activity
- Tobacco smoking and heavy alcohol consumption
- Male gender (men have higher rates of oropharyngeal HPV)
- Immunocompromised states such as HIV infection
- Lack of HPV vaccination
Complications
- Development of oropharyngeal cancers (tonsils, base of tongue)
- Persistent infection leading to chronic inflammation
- Difficulty eating and speaking due to cancer progression
- Spread of cancer to lymph nodes and other organs
- Treatment side effects if cancer develops
Prevention
- HPV vaccination, especially before the onset of sexual activity
- Practicing safe sexual behaviors including condom use
- Limiting number of sexual partners
- Avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol use
- Regular dental and medical checkups for early detection
- Public education on HPV transmission and risks
Treatment Option in Korea
South Korea offers comprehensive care for oropharyngeal HPV infections and associated cancers, including:
- Screening and diagnosis through HPV testing and imaging
- Vaccination programs promoting HPV vaccines for both girls and boys
- Management of precancerous lesions when detected early
- Advanced cancer treatment combining surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy when necessary
- Multidisciplinary care teams including oncologists, infectious disease specialists, and dentists
- Public health campaigns to increase awareness and vaccination coverage
Top Korean medical centers like Severance Hospital, Samsung Medical Center, and National Cancer Center Korea provide expert care, research-driven protocols, and support services for international patients.