Overview
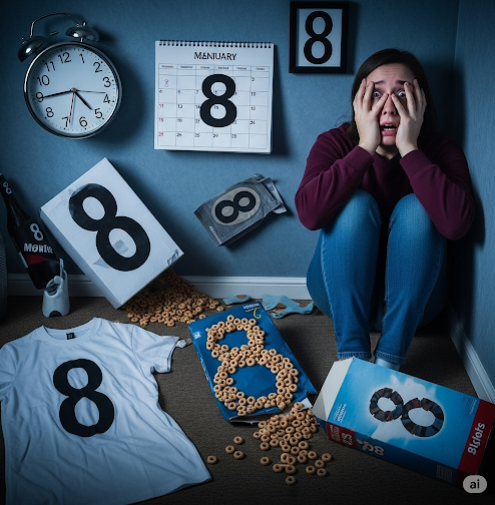
Octophobia is a rare and specific phobia characterized by an intense, irrational fear of the number 8. People with octophobia may experience anxiety, distress, or even panic attacks when they see, think about, or encounter the number 8 in daily life—such as on clocks, license plates, dates, or prices.
While it may seem unusual, octophobia is part of a larger group of numerical phobias, and like other specific phobias, it can interfere with daily functioning and quality of life.
What is Octophobia?
Octophobia is classified as a specific phobia, which is a type of anxiety disorder. The fear is often exaggerated and disproportionate, and individuals with this condition may go out of their way to avoid the number 8 in any context.
This fear may stem from cultural beliefs, traumatic experiences, or underlying anxiety. In some cultures, certain numbers are believed to have symbolic meaning—either positive or negative. In octophobia, the number 8 may be associated with superstition, perfectionism, or infinity, triggering discomfort or fear.
Symptoms
Symptoms of octophobia vary in intensity and can be emotional, physical, or behavioral. Common signs include:
- Rapid heartbeat or shortness of breath when seeing or thinking about the number 8
- Sweating, shaking, or nausea
- Feelings of dread, panic, or anxiety
- Avoidance behaviors, such as skipping house numbers, pages, or dates with 8
- Irritability or agitation when exposed to the number
- Difficulty concentrating due to preoccupation with avoiding 8
In severe cases, individuals may avoid events like birthdays, appointments, or exams scheduled on the 8th day of the month or at 8:00.
Causes
The exact cause of octophobia can vary and may include:
- Traumatic experience associated with the number 8 (e.g., an accident on the 8th)
- Cultural or symbolic associations (e.g., the number 8 symbolizing infinity, cycles, or bad luck in certain belief systems)
- Learned behavior from family or society
- Underlying anxiety disorders or OCD
- Cognitive distortions, where the brain associates the number with danger or negative events
Like other phobias, it may begin in childhood or adolescence, but can also develop later in life.
Risk Factors
You may be at higher risk for developing octophobia if you:
- Have a family history of anxiety or phobias
- Suffer from generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), OCD, or panic disorder
- Were raised in an environment where superstitions were heavily emphasized
- Experienced a traumatic or negative life event involving the number 8
- Have a perfectionistic or highly controlling personality
Complications
If not managed, octophobia can cause:
- Avoidance of important dates, times, or numbers, leading to missed opportunities
- Disruption of daily life, work, or relationships
- Increased general anxiety or development of additional phobias
- Social isolation or embarrassment about the phobia
- Risk of co-occurring disorders, such as depression or OCD
In extreme cases, it can affect financial decisions, communication, or transportation if the person refuses to engage with anything related to the number 8.
Prevention
While octophobia cannot always be prevented, some strategies may reduce the risk:
- Early intervention if signs of irrational fear emerge
- Healthy coping strategies for managing anxiety and stress
- Avoiding reinforcement of superstitions or negative number associations
- Exposure to various numbers during childhood in a neutral or positive context
- Encouraging open discussion about fears and teaching emotional regulation
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea has highly trained professionals in the field of mental health and phobia treatment, with access to modern therapies in both public and private sectors.
1. Psychological Evaluation
- Diagnosis is made by a psychiatrist or psychologist
- Includes clinical interviews, questionnaires, and anxiety assessments
- Rule out co-existing conditions like OCD or generalized anxiety
2. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Most effective treatment for specific phobias
- Helps challenge irrational thoughts about the number 8
- Includes gradual exposure and response prevention techniques
3. Exposure Therapy (Systematic Desensitization)
- Controlled exposure to the number 8 in a safe setting
- Helps reduce fear response over time
- Can be done with images, words, dates, or sounds involving 8
4. Medication (if necessary)
- Anti-anxiety medications (e.g., SSRIs or benzodiazepines)
- Used for short-term symptom control in severe cases
- Typically combined with psychotherapy
5. Supportive Counseling and Group Therapy
- Provides emotional support and coping skills
- Helps reduce isolation or shame
- Group settings may normalize phobic experiences
6. Leading Mental Health Centers in Korea
- National Center for Mental Health (NCMH), Seoul
- Severance Hospital – Psychiatry & Psychology Center
- Samsung Medical Center – Department of Psychiatry
- Asan Medical Center – Anxiety Disorder Unit
- Seoul National University Hospital – Stress and Anxiety Clinic
These facilities provide:
- English-speaking therapists and psychiatrists
- Advanced diagnostic tools and evidence-based therapies
- Multidisciplinary care for patients with complex or rare phobias