Overview
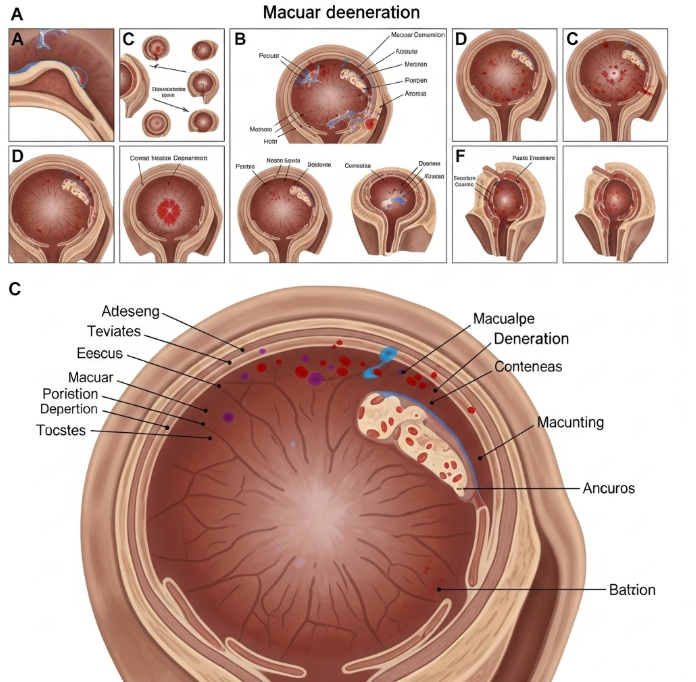
Macular degeneration is a common eye condition that leads to progressive loss of central vision, affecting the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp vision. In Korea, it is increasingly recognized as a major cause of visual impairment, particularly among older adults, and specialized ophthalmology centers provide advanced care and treatment options.
What is Macular Degeneration?
Macular degeneration, often called age-related macular degeneration (AMD), is a degenerative eye disease affecting the macula. It causes blurred or distorted central vision, while peripheral vision often remains intact. AMD can affect both eyes, and its progression varies among individuals.
Symptoms
- Blurred or distorted central vision
- Difficulty recognizing faces or reading small print
- Dark or empty areas in the center of vision
- Distorted or wavy vision (metamorphopsia)
- Need for brighter light when reading or doing close work
- Difficulty adjusting to low-light conditions
Causes
- Aging of retinal tissues
- Accumulation of drusen (yellow deposits) under the retina
- Genetic factors and family history of AMD
- Oxidative stress and retinal damage
- Poor blood flow to the retina
Risk Factors
- Age above 50 years
- Smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke
- Family history of macular degeneration
- High blood pressure or cardiovascular disease
- Obesity and poor diet low in antioxidants
- Excessive UV exposure
Complications
- Permanent loss of central vision
- Difficulty performing daily tasks such as reading or driving
- Increased risk of depression due to vision loss
- Reduced independence in older adults
- Need for low-vision aids for daily activities
Prevention
- Avoid smoking and maintain a healthy lifestyle
- Eat a diet rich in leafy greens, fish, and antioxidants
- Regular eye exams, especially after age 50
- Control blood pressure and manage cardiovascular risk factors
- Protect eyes from excessive sunlight using sunglasses
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Comprehensive eye examination including visual acuity and dilated retinal exam
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT) to visualize macular changes
- Fluorescein angiography to detect abnormal blood vessels
- Genetic testing in select cases with family history
Medical & Surgical Treatments
- Anti-VEGF injections for wet AMD to reduce abnormal blood vessel growth
- Laser therapy to seal leaking vessels in some cases
- Photodynamic therapy using light-activated drugs for abnormal vessels
- Nutritional supplements (AREDS formula) to slow progression in dry AMD
- Low-vision rehabilitation for advanced vision loss
Rehabilitation and Support
- Low-vision aids such as magnifiers, electronic readers, and specialized lighting
- Vision therapy and occupational therapy to adapt daily activities
- Counseling and support groups for patients and families
- Regular monitoring for disease progression