Overview
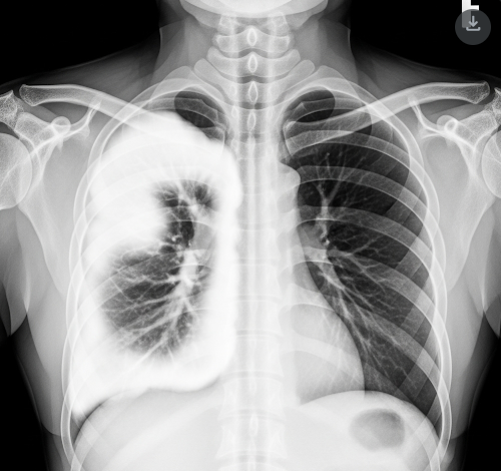
Lobar pneumonia is a type of pneumonia characterized by inflammation and consolidation of an entire lobe of the lung. It is typically caused by bacterial infection, with Streptococcus pneumoniae being the most common culprit. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are vital to prevent complications.
What Is Lobar Pneumonia?
Lobar pneumonia involves infection and inflammation confined to one or more lobes of the lungs, leading to the filling of alveolar spaces with inflammatory exudate. This results in impaired gas exchange and respiratory symptoms. It often follows sudden onset with fever and productive cough.
Symptoms
- High fever and chills
- Productive cough with rusty or purulent sputum
- Chest pain, often pleuritic (sharp and worsens with breathing)
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue and malaise
- Rapid breathing
- Dullness on percussion and decreased breath sounds on the affected lobe
Causes
- Most commonly caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria
- Other bacteria like Haemophilus influenzae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Staphylococcus aureus
- Less commonly viral or fungal pathogens
- Aspiration of oral or gastric contents in some cases
Risk Factors
- Advanced age (elderly)
- Smoking
- Chronic lung diseases (COPD, asthma)
- Immunosuppression (HIV, cancer, chemotherapy)
- Alcoholism
- Recent respiratory infections or viral illnesses
Complications
- Lung abscess
- Pleural effusion and empyema
- Respiratory failure
- Sepsis and systemic infection
- Chronic lung damage or fibrosis
Prevention
- Vaccination against pneumococcus and influenza
- Smoking cessation
- Good hygiene and respiratory etiquette
- Prompt treatment of respiratory infections
- Healthy lifestyle to maintain immune function
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers advanced management for lobar pneumonia including:
- Antibiotic Therapy: Empirical broad-spectrum antibiotics followed by targeted therapy based on culture and sensitivity results.
- Supportive Care: Oxygen therapy, hydration, fever control, and respiratory support as needed.
- Hospitalization: For severe cases requiring close monitoring and intensive care.
- Diagnostic Services: Chest X-rays, sputum cultures, blood tests, and CT scans for accurate diagnosis.
- Rehabilitation: Pulmonary rehabilitation and physiotherapy post-recovery to restore lung function.
With Korea’s advanced healthcare system, patients receive timely diagnosis, effective treatment, and comprehensive supportive care, ensuring favorable outcomes.