Overview
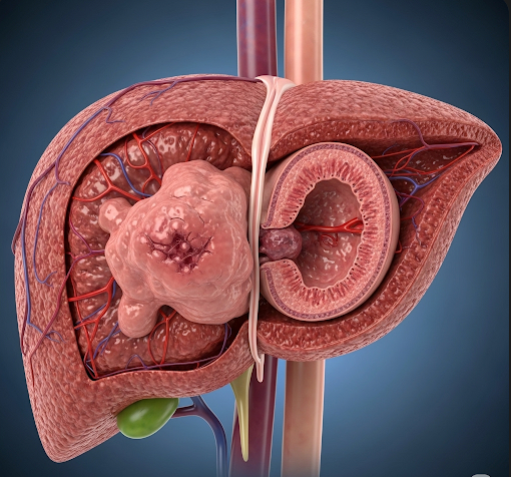
Liver cancer, specifically hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), is the most common primary malignancy of the liver. It arises from liver cells (hepatocytes) and is often associated with chronic liver diseases like hepatitis and cirrhosis. Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving survival rates.
What Is Liver Cancer (Hepatocellular Carcinoma)?
Hepatocellular carcinoma is a malignant tumor originating in the liver’s hepatocytes. It typically develops in the context of chronic liver damage and can grow aggressively, spreading within the liver and beyond. HCC is a major health concern worldwide and requires specialized care.
Symptoms
- Unintentional weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Upper abdominal pain or discomfort
- Enlarged liver or a mass felt under the ribs
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Abdominal swelling due to fluid buildup (ascites)
- Fatigue and weakness
- Nausea and vomiting
Causes
- Chronic infection with hepatitis B virus (HBV) or hepatitis C virus (HCV)
- Liver cirrhosis due to alcohol abuse or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- Exposure to aflatoxins (toxins from certain molds)
- Genetic predisposition and metabolic diseases
- Long-term exposure to toxins and carcinogens
Risk Factors
- Chronic hepatitis B or C infection
- Cirrhosis from any cause
- Heavy alcohol consumption
- Obesity and diabetes
- Family history of liver cancer
- Male gender (higher prevalence)
Complications
- Liver failure
- Metastasis to other organs such as lungs and bones
- Bleeding from ruptured tumors
- Portal vein thrombosis
- Severe ascites and hepatic encephalopathy
Prevention
- Vaccination against hepatitis B virus
- Regular screening for high-risk individuals (e.g., chronic hepatitis or cirrhosis patients)
- Avoiding excessive alcohol intake
- Maintaining healthy weight and controlling diabetes
- Avoiding exposure to aflatoxins in food
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers cutting-edge treatments for liver cancer with multidisciplinary care:
- Surgical Resection: Removal of tumor and surrounding liver tissue in eligible patients.
- Liver Transplantation: Curative option for early-stage HCC with strict criteria.
- Local Ablative Therapies: Radiofrequency ablation (RFA), microwave ablation (MWA), and percutaneous ethanol injection.
- Transarterial Therapies: Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and transarterial radioembolization (TARE) for unresectable tumors.
- Systemic Therapy: Targeted therapies (e.g., sorafenib) and immunotherapy for advanced cases.
- Advanced Diagnostics: High-resolution imaging (CT, MRI) and biomarker tests (AFP levels) for accurate diagnosis and monitoring.
- Supportive Care: Symptom management, nutritional support, and palliative care.
Korean cancer centers combine advanced technology and expert clinical teams to offer personalized treatment plans, improving survival and quality of life for liver cancer patients.