Overview
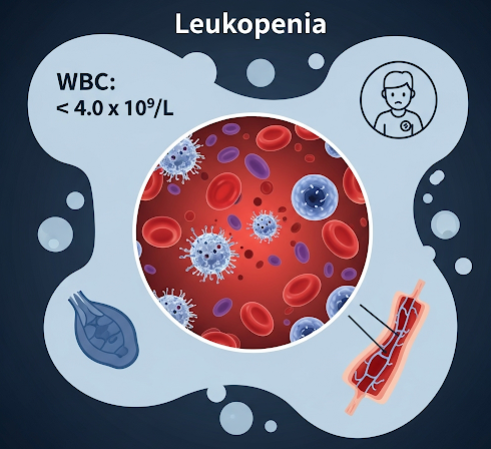
Leukopenia is a medical condition characterized by a decreased number of white blood cells (leukocytes) in the bloodstream, which can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of infections. It is a sign of various underlying conditions and requires careful diagnosis and management.
What Is Leukopenia?
Leukopenia refers to a lower-than-normal white blood cell count, which impairs the body’s ability to fight infections. It can be temporary or chronic and may result from bone marrow problems, autoimmune diseases, infections, or certain medications.
Symptoms
Leukopenia itself may not cause symptoms but increases susceptibility to infections, which can present as:
- Frequent infections
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Mouth ulcers
- Fatigue
- Chills
Causes
- Bone marrow disorders (e.g., aplastic anemia, leukemia)
- Autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus)
- Severe infections that deplete white blood cells
- Certain medications (chemotherapy, antibiotics, antipsychotics)
- Nutritional deficiencies (e.g., vitamin B12, folate)
- Radiation therapy
- Viral infections such as HIV or hepatitis
Risk Factors
- Recent chemotherapy or radiation therapy
- Autoimmune diseases
- Chronic infections
- Poor nutrition
- Genetic disorders affecting blood cell production
Complications
- Increased vulnerability to infections, which can become severe or life-threatening
- Delayed recovery from illnesses
- Potential for sepsis in severe cases
Prevention
- Regular monitoring during chemotherapy or other treatments
- Maintaining good hygiene to reduce infection risk
- Prompt treatment of infections
- Balanced diet with adequate vitamins and minerals
- Avoiding exposure to infectious agents when immune-compromised
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea provides comprehensive care for leukopenia, including:
- Diagnosis: Complete blood count (CBC), bone marrow biopsy, and other tests to identify causes.
- Medications: Growth factors like granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) to stimulate white blood cell production.
- Treatment of Underlying Causes: Managing infections, autoimmune diseases, or discontinuing causative drugs.
- Supportive Care: Infection prevention, hospitalization for severe cases, and close monitoring.
- Nutritional Support: Supplements for vitamin deficiencies.
- Specialist Care: Hematologists and immunologists provide personalized treatment plans.
Korea’s advanced healthcare system ensures accurate diagnosis and effective treatment of leukopenia to protect patients from infections and improve quality of life.