Overview
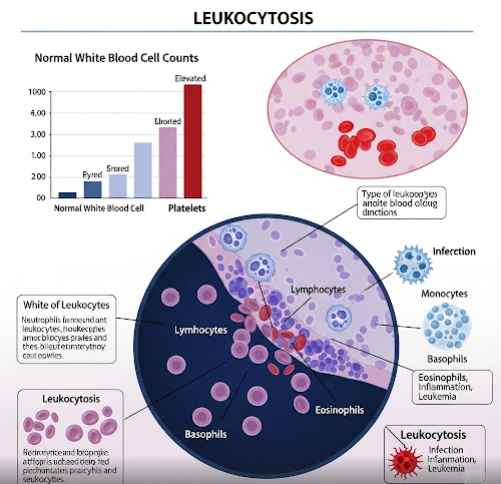
Leukocytosis is a condition characterized by an elevated white blood cell (WBC) count in the bloodstream, often indicating an underlying response to infection, inflammation, or other medical conditions. It is not a disease itself but a sign that requires further evaluation to determine its cause.
What Is Leukocytosis?
Leukocytosis refers to a higher-than-normal level of white blood cells, which are crucial components of the immune system responsible for fighting infections and foreign substances. It can result from various physiological or pathological conditions and may be transient or persistent.
Symptoms
Leukocytosis itself typically does not cause symptoms, but underlying conditions may present with:
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Signs of infection (e.g., cough, sore throat)
- Inflammation-related symptoms (e.g., swelling, redness)
Causes
- Infections (bacterial, viral, fungal)
- Inflammatory diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease)
- Stress or intense physical activity
- Leukemia or other blood cancers
- Tissue damage (e.g., trauma, burns)
- Medications such as corticosteroids
- Smoking
Risk Factors
- Recent infections or illness
- Chronic inflammatory conditions
- Exposure to toxins or radiation
- History of blood disorders
- Smoking and lifestyle factors
Complications
- Leukocytosis itself rarely causes complications but indicates potential serious underlying issues that need diagnosis.
- In cases related to leukemia or severe infection, complications depend on the specific disease.
Prevention
- Managing underlying causes effectively (e.g., infections, chronic diseases)
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle to reduce infection risk
- Avoiding exposure to harmful chemicals or radiation
- Regular medical checkups for early detection of blood abnormalities
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers thorough evaluation and management for leukocytosis through:
- Diagnostic Testing: Complete blood count (CBC), blood smear, bone marrow biopsy, and infection screening to identify causes.
- Treating Underlying Conditions: Antibiotics for infections, anti-inflammatory medications for autoimmune diseases, or chemotherapy for leukemia.
- Specialist Care: Hematologists and internal medicine specialists provide tailored treatment plans.
- Monitoring: Regular follow-up to track WBC levels and response to treatment.
- Advanced Laboratory Services: Access to molecular and genetic testing for precise diagnosis.
With Korea’s advanced diagnostic facilities and expert medical teams, leukocytosis patients receive prompt, accurate evaluation and personalized care.