Overview
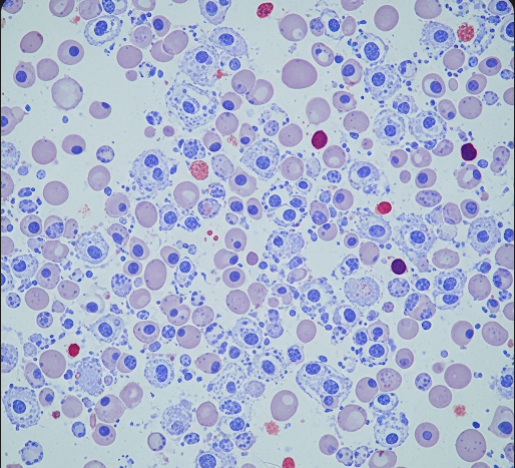
Leukemia is a type of cancer that originates in the blood-forming tissues, primarily the bone marrow, leading to the uncontrolled production of abnormal white blood cells. These abnormal cells interfere with normal blood cell functions, causing a range of symptoms and complications. Early diagnosis and effective treatment are crucial for improved outcomes.
What Is Leukemia?
Leukemia refers to a group of blood cancers characterized by the rapid proliferation of immature or abnormal white blood cells. It can be classified into acute or chronic forms, and further divided into lymphocytic or myeloid types, each with distinct clinical features and treatment approaches.
Symptoms
- Fatigue and weakness
- Frequent infections
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Pale skin (anemia)
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Bone or joint pain
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fever or night sweats
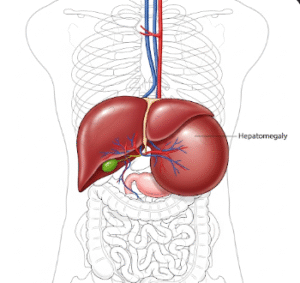
- Enlarged spleen or liver
Causes
- Genetic mutations in blood cells leading to uncontrolled growth
- Exposure to high levels of radiation or certain chemicals (e.g., benzene)
- Previous chemotherapy or radiation therapy for other cancers
- Certain genetic disorders such as Down syndrome
Risk Factors
- Age (more common in older adults, but some types affect children)
- Family history of leukemia or other cancers
- Exposure to environmental toxins and radiation
- Smoking
- Certain viral infections
Complications
- Severe infections due to low white blood cell count
- Anemia and bleeding problems due to low red blood cells and platelets
- Organ enlargement and dysfunction
- Side effects from treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation
- Risk of relapse or secondary cancers
Prevention
- Avoid exposure to known carcinogens such as tobacco smoke and toxic chemicals
- Use protective equipment in high-risk environments
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle with balanced nutrition and exercise
- Regular medical checkups for early detection, especially in high-risk groups
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers comprehensive, state-of-the-art leukemia care with multidisciplinary approaches:
- Chemotherapy: Intensive drug regimens to kill cancerous cells, tailored to leukemia subtype.
- Targeted Therapy: Use of drugs that specifically target molecular abnormalities in leukemia cells.
- Radiation Therapy: Sometimes used to prepare for bone marrow transplant or to treat affected areas.
- Bone Marrow/Stem Cell Transplant: Curative option for eligible patients, with advanced transplant centers in Korea.
- Supportive Care: Management of infections, anemia, and side effects.
- Clinical Trials: Access to innovative therapies and new drug trials at leading Korean medical institutions.
- Psychosocial Support: Counseling and rehabilitation services to improve quality of life.
Korea’s advanced healthcare infrastructure and expert oncology teams provide personalized treatment plans, enhancing survival and patient well-being.