Overview
Leptospirosis is a bacterial infection caused by Leptospira species, typically transmitted through contact with water contaminated by the urine of infected animals. It affects humans worldwide and can cause a wide range of symptoms, from mild flu-like illness to severe organ damage.
What Is Leptospirosis?
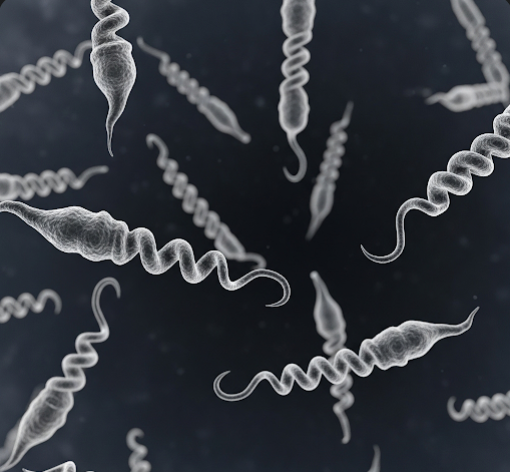
Leptospirosis is a zoonotic disease caused by spiral-shaped bacteria called Leptospira. Humans usually contract it by exposure to contaminated water or soil, especially in tropical and subtropical regions. The bacteria enter the body through cuts, mucous membranes, or ingestion.
Symptoms
- High fever
- Headache
- Muscle aches (especially calves)
- Vomiting
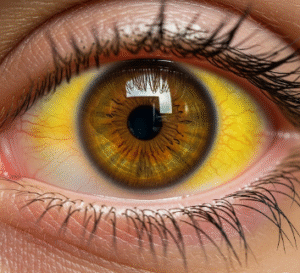
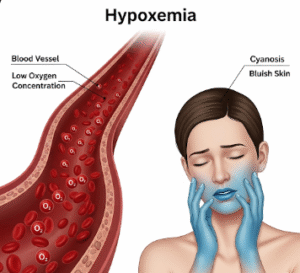
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes)
- Red eyes (conjunctival suffusion)
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea
- Rash (in some cases)
Symptoms usually appear 2 days to 4 weeks after exposure.
Causes
- Contact with water, soil, or food contaminated with urine from infected animals such as rodents, cattle, pigs, and dogs.
- Occupational exposure (farmers, sewer workers, veterinarians).
- Recreational activities in contaminated water bodies.
Risk Factors
- Working or living in tropical or subtropical climates
- Occupations involving contact with animals or contaminated water
- Exposure to floodwaters or poor sanitation
- Outdoor recreational activities like swimming or fishing in freshwater
Complications
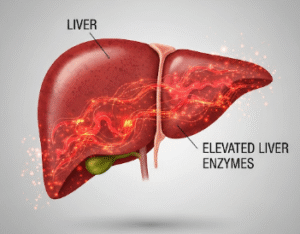
- Weil’s disease: severe form with kidney and liver failure
- Meningitis or inflammation of the brain and spinal cord membranes
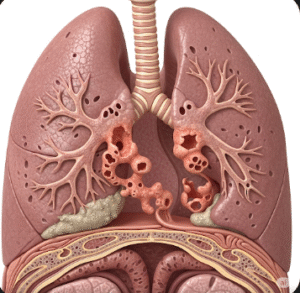
- Respiratory distress or pulmonary hemorrhage
- Muscle inflammation (myositis)
- Death in severe cases if untreated
Prevention
- Avoid swimming or wading in potentially contaminated water
- Use protective clothing and footwear when exposed to contaminated environments
- Control rodent populations near living and working areas
- Maintain good hygiene and clean water supplies
- Vaccination for animals in endemic areas
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers modern and effective management for leptospirosis, including:
- Antibiotic Therapy: Early administration of antibiotics such as doxycycline, penicillin, or ceftriaxone to reduce severity.
- Supportive Care: Hospitalization for severe cases requiring intravenous fluids, dialysis, or respiratory support.
- Diagnostic Services: Laboratory tests including blood cultures, PCR, and serological testing to confirm infection.
- Public Health Measures: Surveillance and control programs to reduce outbreaks and educate at-risk populations.
- Occupational Health Support: Protective guidelines and medical screening for high-risk workers.
With Korea’s advanced healthcare infrastructure, patients with leptospirosis receive timely diagnosis and effective treatment to ensure full recovery.