Overview
Leprosy, also known as Hansen’s disease, is a chronic infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium leprae. It primarily affects the skin, peripheral nerves, mucous membranes, and eyes. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent nerve damage and disability.
What Is Leprosy (Hansen’s Disease)?
Leprosy is a slow-progressing bacterial infection that mainly targets the skin and nerves, leading to skin lesions, numbness, and muscle weakness. The disease is curable with multidrug therapy (MDT), and early treatment reduces the risk of complications.
Symptoms
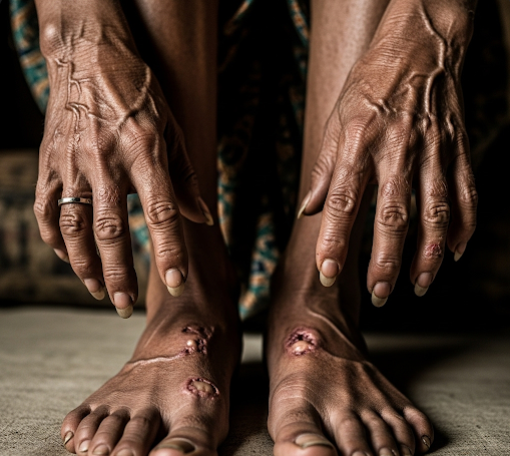
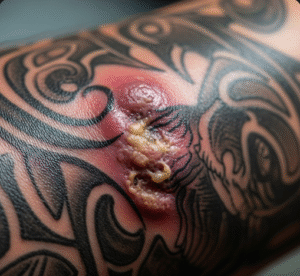
- Pale or reddish skin patches with reduced sensation
- Numbness or loss of feeling in hands, feet, and other affected areas
- Muscle weakness or paralysis
- Thickened nerves, especially around elbows and knees
- Eye problems leading to dryness or vision loss
- Nosebleeds or nasal congestion in some cases
Causes
- Infection with Mycobacterium leprae bacteria
- Transmission through prolonged close contact via respiratory droplets or skin contact
Risk Factors
- Living in or traveling to endemic regions (South Asia, Africa, Latin America)
- Close and prolonged contact with untreated individuals
- Weakened immune system
- Genetic susceptibility
Complications
- Permanent nerve damage causing loss of sensation
- Muscle weakness and deformities
- Blindness from eye involvement
- Secondary infections from wounds due to numbness
- Social stigma and psychological impact
Prevention
- Early diagnosis and prompt treatment of cases
- Avoiding prolonged close contact with untreated individuals
- BCG vaccination may provide some protection
- Public health education to reduce stigma and encourage treatment
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers comprehensive care for leprosy, including:
- Multidrug Therapy (MDT): WHO-recommended combination of dapsone, rifampicin, and clofazimine to cure the infection.
- Neurological Care: Management of nerve damage and rehabilitation.
- Support Services: Psychological counseling and social support to combat stigma.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Skin biopsy, smear tests, and PCR for accurate diagnosis.
- Public Health Programs: Korea’s health system supports awareness, screening, and treatment to prevent spread.
Though rare in Korea, the country’s advanced healthcare system is well-equipped to diagnose, treat, and support patients with leprosy effectively.