Overview
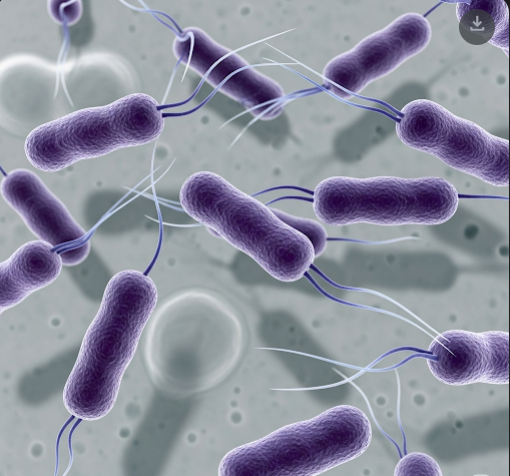
Legionnaires’ disease is a severe form of pneumonia caused by the Legionella bacteria, which thrive in water systems like cooling towers, hot tubs, and plumbing. It primarily affects the lungs, causing serious respiratory illness, especially in older adults and those with weakened immune systems.
What Is Legionnaires’ Disease?
Legionnaires’ disease is a type of bacterial pneumonia resulting from inhaling aerosolized water droplets contaminated with Legionella pneumophila. It can cause severe lung infection requiring prompt medical treatment to prevent complications and death.
Symptoms
- High fever (often above 39°C or 102°F)
- Chills and shaking
- Cough (may produce mucus or blood)
- Shortness of breath
- Muscle aches
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Confusion or mental changes (in severe cases)
- Gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
Causes
- Infection by inhaling water droplets containing Legionella bacteria
- Contaminated water sources such as air conditioning systems, hot tubs, fountains, and plumbing
- Aspiration of contaminated water in hospital settings
Risk Factors
- Age over 50 years
- Smoking
- Chronic lung disease (e.g., COPD, asthma)
- Weakened immune system (due to illness or medications)
- Recent hospitalization or long-term care facility residence
- Travel history involving hotels or cruise ships with poorly maintained water systems
Complications
- Respiratory failure
- Septic shock
- Kidney failure
- Lung abscess
- Multi-organ failure
- Death if untreated or in severe cases
Prevention
- Proper maintenance and disinfection of water systems in buildings and healthcare facilities
- Regular inspection of cooling towers, hot tubs, and plumbing
- Avoiding smoking and managing chronic lung diseases
- Prompt identification and treatment of outbreaks
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers advanced healthcare services for Legionnaires’ disease, including:
- Antibiotic Therapy: Use of macrolides (e.g., azithromycin) or fluoroquinolones (e.g., levofloxacin) as first-line treatments.
- Hospital Care: Supportive treatments including oxygen therapy, intravenous fluids, and intensive care for severe cases.
- Diagnostic Testing: Rapid identification through sputum culture, urinary antigen test, and PCR testing.
- Infection Control: Korean hospitals follow strict infection prevention protocols to minimize nosocomial cases.
- Public Health Surveillance: National monitoring to quickly detect and respond to outbreaks.
With expert infectious disease specialists and modern medical facilities, Korea ensures effective treatment and control of Legionnaires’ disease.