Overview
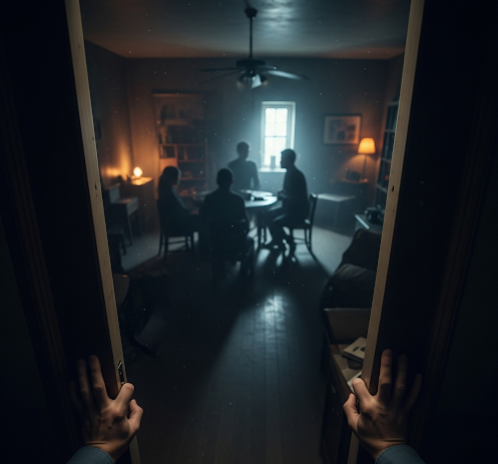
Koinoniphobia is a specific phobia characterized by an intense, irrational fear of rooms, especially those filled with people, or fear of being in enclosed spaces where social interaction occurs. This condition can significantly interfere with daily life, limiting social interactions, work, and activities that involve enclosed or crowded environments. Although relatively rare, koinoniphobia can cause considerable distress. In Korea, mental health professionals provide specialized psychological and psychiatric treatments to help individuals manage and overcome this debilitating fear.
What Is Koinoniphobia?
Koinoniphobia is an anxiety disorder where the affected person experiences overwhelming fear or panic when inside rooms or enclosed spaces, particularly when other people are present. The phobia may manifest as avoidance behavior, distress upon entering rooms, or physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat, sweating, trembling, and shortness of breath. It differs from claustrophobia, which is fear of confined spaces, by focusing on the social and spatial aspect of rooms and their occupants.
Symptoms
- Intense fear or anxiety upon entering or being inside rooms with people
- Avoidance of enclosed spaces such as classrooms, meeting rooms, or social gatherings
- Physical symptoms including:
- Heart palpitations
- Sweating
- Trembling or shaking
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Nausea
- Dry mouth
- Psychological symptoms such as overwhelming dread, fear of losing control, or a sense of impending doom
- Difficulty concentrating and desire to escape the situation
Causes
The exact cause of koinoniphobia is unclear but may involve a combination of factors:
- Traumatic or negative experiences associated with enclosed spaces or social settings
- Genetic predisposition to anxiety disorders or phobias
- Learned behavior from observing fearful responses in others
- Underlying social anxiety disorder or other psychiatric conditions
- Brain chemistry imbalances affecting fear and anxiety regulation
Risk Factors
- Personal or family history of anxiety disorders or phobias
- Past traumatic events in enclosed or crowded spaces
- High levels of stress or major life changes
- Social isolation or limited social support
- Coexisting mental health issues such as panic disorder or agoraphobia
Complications
- Severe social withdrawal and isolation
- Impaired academic, occupational, or social functioning
- Increased risk of depression and other anxiety disorders
- Reduced quality of life and daily functioning
- Physical health problems due to chronic stress and anxiety
Prevention
- Early intervention for anxiety symptoms and phobias
- Stress management and coping skills development
- Supportive social environments and gradual exposure to feared situations
- Psychological education to reduce stigma and encourage help-seeking
- Healthy lifestyle choices including regular exercise, balanced diet, and adequate sleep
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean mental health services offer a range of effective treatments tailored to individuals with koinoniphobia:
- Psychotherapy:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps patients identify and challenge irrational fears, and gradually expose themselves to feared environments through controlled, stepwise exposure therapy.
- Exposure Therapy: Systematic and gradual exposure to rooms and social settings to reduce fear response over time.
- Mindfulness-Based Therapies: Techniques to manage anxiety symptoms and improve emotional regulation.
- Medications:
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or other antidepressants to reduce anxiety and improve mood
- Benzodiazepines for short-term relief of severe anxiety symptoms under careful medical supervision
- Supportive Care:
- Psychoeducation for patients and families about the nature of phobias and treatment strategies
- Group therapy or support groups to reduce social isolation and build coping skills
- Integrated Approach:
- Coordination among psychiatrists, psychologists, and counselors for comprehensive care
- Continuous monitoring and adjustment of therapy plans to ensure progress
Korea’s modern mental health infrastructure emphasizes patient-centered care, combining evidence-based therapies and culturally sensitive approaches to help individuals overcome koinoniphobia and regain functional, fulfilling lives.