Overview
Klatskin tumor, also known as hilar cholangiocarcinoma, is a rare and aggressive cancer that arises at the junction where the right and left hepatic bile ducts meet near the liver hilum. It is a form of bile duct cancer that primarily affects the biliary tract and is associated with poor prognosis due to its location and late presentation. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for improving survival. Korea’s leading hepatobiliary centers specialize in advanced diagnostic techniques, surgical resection, and multidisciplinary care to manage this challenging condition effectively.
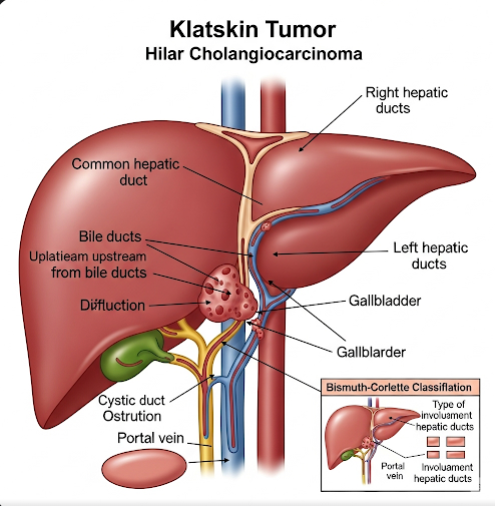
What Is Klatskin Tumor (Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma)?
Klatskin tumor is a type of cholangiocarcinoma that originates in the bile ducts at the hepatic hilum, the area where the main bile ducts exit the liver. It causes obstruction of bile flow, leading to jaundice and liver dysfunction. This tumor is classified based on the extent and location of bile duct involvement and may invade adjacent blood vessels and liver tissue. Due to its anatomical complexity, treatment is often challenging and requires specialized surgical expertise.
Symptoms
Symptoms typically develop gradually as bile duct obstruction worsens and may include:
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Dark urine and pale stools
- Itching (pruritus) caused by bile salt accumulation
- Abdominal pain or discomfort, particularly in the upper right quadrant
- Unintended weight loss and loss of appetite
- Fever and chills if secondary infection (cholangitis) occurs
- Fatigue and general malaise
Causes
The exact cause of Klatskin tumor remains unclear but several risk factors and conditions predispose to its development:
- Chronic inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts (primary sclerosing cholangitis)
- Bile duct cysts or congenital anomalies
- Chronic liver diseases including hepatitis B and C infections
- Exposure to liver fluke parasites, common in some regions
- Smoking and exposure to certain chemicals
- Genetic mutations leading to uncontrolled cell growth in bile duct lining
Risk Factors
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC)
- Chronic viral hepatitis and cirrhosis
- Bile duct cysts (choledochal cysts)
- Liver fluke infestation (Clonorchis sinensis) prevalent in East Asia
- Older age, usually affecting people over 50 years
- Smoking and occupational exposure to carcinogens
- Family history of biliary tract cancers
Complications
- Progressive bile duct obstruction leading to liver failure
- Recurrent cholangitis (bile duct infections)
- Jaundice-related complications including severe itching and fat malabsorption
- Spread (metastasis) to lymph nodes, liver, lungs, and peritoneum
- Poor nutritional status due to impaired digestion and appetite loss
Prevention
- Managing and monitoring chronic liver and bile duct diseases closely
- Avoiding risk factors such as smoking and liver fluke exposure
- Early treatment of bile duct infections and inflammation
- Regular screening in high-risk individuals with PSC or bile duct cysts
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and liver health
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers specialized, multidisciplinary care for Klatskin tumors with advanced expertise and technology:
- Surgical Resection:
- The main curative treatment involves complex surgery to remove the tumor and affected bile ducts, often combined with partial liver resection (hepatectomy).
- Surgery requires expert hepatobiliary surgeons due to proximity to major blood vessels and liver structures.
- Preoperative portal vein embolization may be performed to improve liver regeneration post-surgery.
- Biliary Drainage Procedures:
- Endoscopic or percutaneous biliary stenting to relieve obstruction and improve liver function before surgery or as palliative treatment.
- Chemotherapy and Radiation:
- Adjuvant chemotherapy or chemoradiation may be given postoperatively to reduce recurrence risk.
- For inoperable cases, systemic therapies help control disease progression.
- Liver Transplantation:
- Select cases with early-stage disease and strict criteria may be candidates for liver transplantation combined with neoadjuvant therapy.
- Advanced Imaging and Diagnostics:
- High-resolution MRI, MRCP (magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography), CT scans, and PET scans are employed for precise staging and surgical planning.
- Multidisciplinary Approach:
- Treatment teams include hepatobiliary surgeons, oncologists, radiologists, gastroenterologists, and supportive care specialists for optimal outcomes.
Korean medical centers are recognized globally for their expertise in managing complex hepatobiliary cancers, combining modern surgical techniques with innovative systemic therapies to improve patient survival and quality of life.