Overview
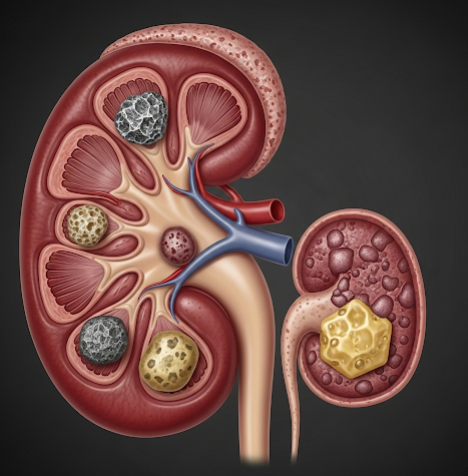
Kidney stones, medically known as nephrolithiasis or renal calculi, are hard deposits formed from minerals and salts that crystallize within the kidneys. These stones can vary in size and shape, causing pain, urinary obstruction, and sometimes infections. Kidney stones are a common urological condition worldwide, and Korea offers advanced diagnostic imaging and state-of-the-art treatments including minimally invasive surgery and extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) to effectively manage and prevent recurrence.
What Are Kidney Stones?
Kidney stones are solid concretions or crystal aggregations formed in the kidneys from dietary minerals and waste products in the urine. When urine becomes concentrated, these minerals can crystallize and form stones. Stones may remain in the kidney or travel down the urinary tract causing pain and blockage. Types of stones include calcium oxalate, uric acid, struvite, and cystine stones, each having different causes and treatment approaches.
Symptoms
Symptoms often occur when stones move into the urinary tract and include:
- Severe, sharp pain in the back or side (renal colic)
- Pain radiating to the lower abdomen and groin
- Hematuria (blood in urine), sometimes visible or microscopic
- Frequent, painful urination or urgency
- Nausea and vomiting due to severe pain
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine if infection is present
- Fever and chills indicating possible infection
Causes
Kidney stones form due to an imbalance in the substances that make up urine, including:
- High levels of calcium, oxalate, or uric acid
- Low urine volume leading to concentrated urine
- Certain metabolic disorders increasing stone-forming substances
- Urinary tract infections, especially with urease-producing bacteria
- Diet high in salt, protein, or oxalate-rich foods
- Dehydration reducing urine flow
Risk Factors
- Family history of kidney stones
- Dehydration or low fluid intake
- Diet high in sodium, animal protein, or oxalate-rich foods
- Obesity and metabolic syndrome
- Certain medical conditions such as gout, hyperparathyroidism, or inflammatory bowel disease
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Recurrent urinary tract infections
Complications
- Urinary tract obstruction causing severe pain and kidney damage
- Recurrent infections and pyelonephritis
- Hydronephrosis (swelling of the kidney due to urine buildup)
- Chronic kidney disease if obstruction or infections are untreated
- Persistent hematuria and bladder irritation
Prevention
- Maintain adequate hydration, aiming for at least 2-3 liters of water daily
- Dietary modifications to reduce salt, animal protein, and oxalate intake
- Balanced calcium intake to prevent excess oxalate absorption
- Regular physical activity to improve metabolism
- Medical management for underlying metabolic disorders
- Monitoring and follow-up for individuals with history of stones
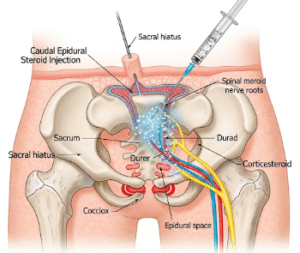
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea’s medical centers are equipped with advanced technology and expert specialists to treat kidney stones effectively:
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL): Non-invasive treatment using shock waves to break stones into smaller fragments that can pass naturally.
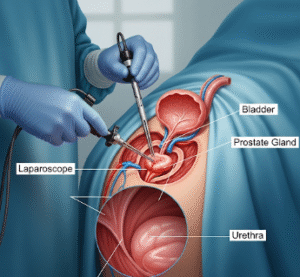
- Ureteroscopy: A minimally invasive endoscopic procedure to remove or fragment stones lodged in the ureter or kidney using laser lithotripsy.
- Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL): Surgical removal of large or complex kidney stones through a small incision in the back, performed under general anesthesia.
- Medical Expulsive Therapy: Use of medications such as alpha-blockers to facilitate stone passage in smaller stones.
- Pain Management and Supportive Care: Including hydration, analgesics, and anti-nausea medications.
- Dietary Counseling: Korean dietitians provide personalized plans to reduce recurrence risk based on stone composition and patient lifestyle.
Regular imaging and metabolic evaluation in Korea’s specialized urology clinics help detect early recurrence and guide prevention strategies. The integration of modern technology and multidisciplinary care ensures optimal outcomes and minimal complications for patients with kidney stones.