Overview
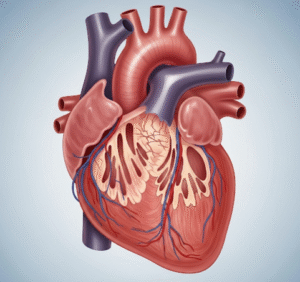
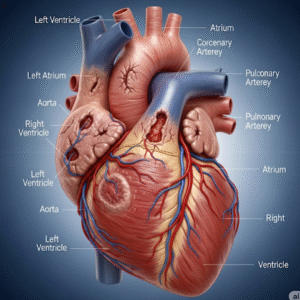
Junctional Tachycardia (JT) is a type of cardiac arrhythmia in which rapid heartbeats originate from the atrioventricular (AV) junction instead of the sinoatrial (SA) node. This arrhythmia can result in palpitations, dizziness, or shortness of breath and is more commonly observed in hospitalized patients or those with underlying heart conditions. In South Korea, JT is managed in advanced cardiology centers with specialized electrophysiology services, ensuring accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
What is Junctional Tachycardia?
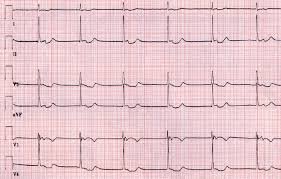
Junctional Tachycardia is an abnormal rhythm caused by rapid electrical impulses generated by the AV junction. Unlike normal sinus tachycardia, the SA node does not control the heart rate. The ventricular rate usually ranges from 100 to 180 beats per minute. JT can be paroxysmal (sudden onset) or persistent, and may occur in children, adults, or patients after cardiac surgery.
Symptoms
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue or weakness
- Chest discomfort
- Fainting or syncope in severe cases
Causes
- Excessive automaticity of the AV junction
- Heart surgery or post-operative stress
- Myocardial ischemia or heart disease
- Certain medications, including digoxin toxicity
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Congenital heart conditions in children
Risk Factors
- History of cardiac surgery
- Structural heart disease
- Electrolyte disturbances
- Use of medications affecting heart rhythm
- Advanced age or underlying cardiovascular conditions
Complications
- Rapid heart rate leading to decreased cardiac output
- Syncope or fainting episodes
- Development of other arrhythmias
- Worsening of underlying heart conditions
- Rarely, heart failure if left untreated
Prevention
- Regular cardiac evaluations and monitoring
- Managing underlying heart conditions such as hypertension or coronary artery disease
- Avoiding medications or substances that trigger arrhythmias without medical guidance
- Maintaining electrolyte balance and healthy lifestyle habits
- Early medical attention for palpitations or irregular heartbeat
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides modern management for Junctional Tachycardia:
- Diagnosis: ECG and Holter monitoring are primary diagnostic tools. Advanced cardiac centers like Seoul National University Hospital, Asan Medical Center, and Samsung Medical Center perform detailed rhythm analysis.
- Medical Management: Antiarrhythmic medications (e.g., beta-blockers, amiodarone) are used to control heart rate. Correction of electrolyte imbalances and adjustment of causative drugs are essential.
- Catheter Ablation: For recurrent or symptomatic JT, catheter ablation may be performed to destroy the abnormal electrical pathway. Major Korean hospitals have experienced electrophysiology teams specializing in ablation procedures.
- Pacemaker or Defibrillator Therapy: Rarely, patients with persistent arrhythmias may require pacemaker implantation. Advanced electrophysiology labs in Korea handle such procedures safely.
- Follow-Up and Rehabilitation: Cardiac rehabilitation and regular follow-up visits help monitor rhythm, prevent recurrence, and manage associated cardiovascular conditions. Hospitals provide comprehensive post-treatment care and lifestyle counseling.