Overview
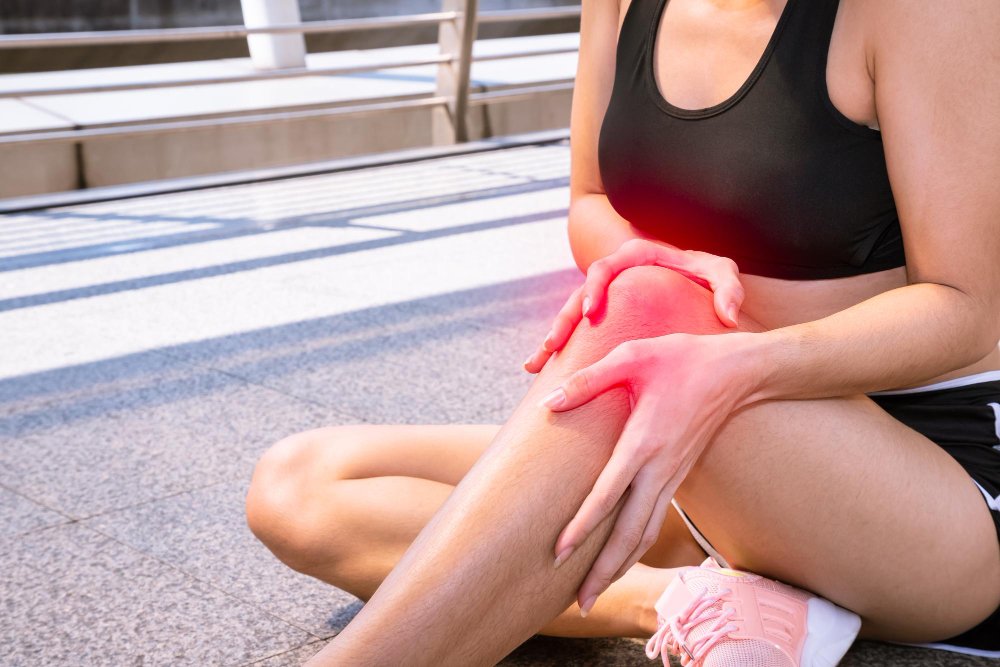
Joint inflammation, also known as arthritis, refers to swelling, pain, and stiffness in one or more joints. It is a common condition that can affect people of all ages, ranging from temporary injury-related inflammation to chronic autoimmune disorders. In South Korea, joint inflammation is widely treated in orthopedic, rheumatology, and sports medicine clinics, with advanced diagnostic and therapeutic options available at hospitals like Seoul National University Hospital, Samsung Medical Center, and Asan Medical Center.
What is Joint Inflammation?
Joint inflammation occurs when the tissues within a joint become irritated, swollen, or painful. This can result from injury, infection, autoimmune disease, or degenerative processes. Common types include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile arthritis, and reactive arthritis. Inflammation can affect the synovium (joint lining), cartilage, and surrounding tissues, leading to pain, stiffness, and impaired function.
Symptoms
- Pain or tenderness in one or more joints
- Swelling and warmth over affected joints
- Stiffness, especially in the morning or after inactivity
- Redness around the joint in some cases
- Reduced range of motion and difficulty moving the joint
- Fatigue or malaise in systemic inflammatory conditions
Causes
- Autoimmune diseases, e.g., rheumatoid arthritis or juvenile idiopathic arthritis
- Degenerative joint disease, e.g., osteoarthritis
- Infections, including bacterial or viral arthritis
- Trauma or repetitive stress injuries
- Metabolic disorders, such as gout or pseudogout
Risk Factors
- Older age (higher risk of osteoarthritis)
- Family history of autoimmune or inflammatory joint diseases
- Previous joint injuries
- Obesity or excess weight increasing joint stress
- Sedentary lifestyle or lack of muscle strength around joints
- Chronic illnesses, including diabetes or cardiovascular disease
Complications
- Chronic pain and disability
- Joint deformity or reduced mobility
- Muscle weakness due to disuse
- Osteoporosis or bone density loss from prolonged inflammation or medication
- Systemic complications in autoimmune conditions, e.g., heart or lung involvement
Prevention
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce joint stress
- Regular low-impact exercise to strengthen muscles around joints
- Early treatment of injuries or joint pain
- Avoiding repetitive stress and protecting joints during sports
- Balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory nutrients (omega-3, antioxidants)
- Regular check-ups for individuals with autoimmune conditions or family history
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides advanced care for joint inflammation through orthopedic, rheumatology, and rehabilitation centers:
- Diagnosis:
- Physical examination and patient history
- Blood tests for inflammation markers and autoimmune antibodies
- X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound to assess joint damage and inflammation
- Medical Management:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain and swelling
- Corticosteroids for acute inflammation
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) or biologics for autoimmune arthritis
- Medications are carefully monitored for side effects
- Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation:
- Exercises to maintain joint mobility and muscle strength
- Occupational therapy for daily activity assistance
- Heat or cold therapy to relieve pain and stiffness
- Surgical Interventions:
- Joint replacement or arthroscopy for severe degenerative or inflammatory damage
- Performed at advanced centers like Samsung Medical Center and Asan Medical Center
- Follow-Up Care:
- Regular monitoring of disease activity and joint function
- Adjustment of medications and therapy based on response
- Long-term rehabilitation programs to maintain quality of life