Overview
Jock itch, medically known as Tinea Cruris, is a common fungal infection that affects the skin of the groin, inner thighs, and buttocks. In South Korea, it frequently occurs in athletes, men who sweat excessively, or individuals with warm, humid conditions. Dermatology clinics across the country, including Seoul National University Hospital, Samsung Medical Center, and Asan Medical Center, provide effective diagnosis and treatment using topical and systemic antifungal therapies.
What is Jock Itch?
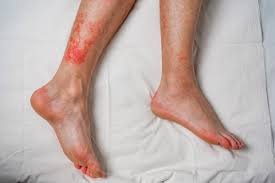
Jock itch is a superficial fungal infection caused by dermatophytes, commonly Trichophyton species. It leads to itchy, red, and sometimes scaly skin lesions. Although it primarily affects men, women can also develop the condition. Jock itch is contagious and can spread through direct skin contact, contaminated clothing, or towels.
Symptoms
- Red, itchy rash in the groin, inner thighs, or buttocks
- Scaling or flaking skin
- Burning or stinging sensation
- Darker skin may show discolored patches
- Rash may extend outward with raised edges
- Mild odor in some cases
Causes
- Infection by dermatophyte fungi, especially Trichophyton species
- Warm, moist environments such as sweaty clothing or locker rooms
- Poor personal hygiene
- Sharing contaminated towels, clothing, or sports equipment
- Obesity or skin folds increasing moisture accumulation
Risk Factors
- Male sex (more common in men)
- Participation in sports or physical activity causing sweating
- Warm and humid climates or indoor conditions
- Compromised immune system or chronic health conditions
- Tight clothing that traps moisture
Complications
- Secondary bacterial infection due to scratching
- Chronic or recurrent infections if untreated
- Spread to surrounding areas, including thighs, buttocks, or abdomen
- Skin discoloration or mild scarring in severe cases
Prevention
- Maintain good personal hygiene and keep groin area clean and dry
- Change sweaty clothing promptly
- Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing
- Avoid sharing towels, clothing, or sports gear
- Use antifungal powders or sprays prophylactically in high-risk situations
- Regular laundering of undergarments and athletic wear
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers effective management of jock itch through dermatology clinics and specialized hospitals:
- Diagnosis:
- Clinical examination of affected skin
- Fungal culture or KOH test for confirmation in uncertain cases
- Assessment of severity and extent of spread
- Medical Management:
- Topical antifungal creams or ointments (e.g., clotrimazole, terbinafine)
- Oral antifungal medications for severe or resistant cases
- Symptomatic relief with soothing lotions or anti-itch medications
- Education on hygiene and preventive measures
- Specialized Care in Korean Hospitals:
- Seoul National University Hospital: Dermatology departments providing accurate diagnosis and treatment
- Samsung Medical Center: Advanced management for chronic or recurrent fungal infections
- Asan Medical Center: Comprehensive dermatology care including follow-up and patient education
- Follow-Up Care:
- Monitor for recurrence or secondary infections
- Continue topical treatment as prescribed to ensure complete clearance
- Maintain preventive hygiene measures to reduce risk of reinfection