Overview
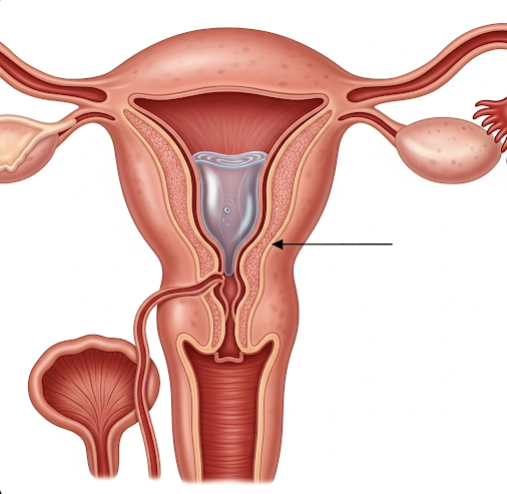
Isthmocele, also known as a cesarean scar defect or uterine niche, is a defect or pouch-like indentation that forms at the site of a previous cesarean section (C-section) scar in the lower uterine segment. It occurs when the uterine wall does not heal properly after the surgical incision, leading to a thinning or disruption of the myometrium (muscle layer). This condition has become increasingly recognized as cesarean deliveries rise globally, including in Korea. Isthmocele can cause various gynecological symptoms and impact fertility, making its diagnosis and management important for women’s reproductive health.
What is Isthmocele?
An isthmocele is essentially a small diverticulum or pocket at the site of a cesarean scar where the uterine muscle has not fully regenerated, resulting in a weakened or thinned area. This niche can trap menstrual blood or secretions, leading to abnormal uterine bleeding and other complications.
While many women with isthmocele may be asymptomatic, the condition can contribute to problems such as postmenstrual spotting, pelvic pain, infertility, and increased risk of uterine rupture in subsequent pregnancies.
Symptoms
Symptoms of isthmocele vary depending on its size and associated complications, but common complaints include:
- Postmenstrual spotting or prolonged menstrual bleeding: Blood can pool in the niche and slowly drain, causing spotting for days after menstruation.
- Pelvic pain or discomfort: Especially during menstruation or intercourse.
- Infertility or difficulty conceiving: The niche can interfere with sperm transport or embryo implantation.
- Abnormal vaginal discharge: Due to trapped blood and secretions.
- Dysmenorrhea: Painful menstruation.
- Rarely, uterine rupture: In future pregnancies if the scar is significantly weakened.
- Menstrual irregularities: Including intermenstrual bleeding.
Some women may remain symptom-free and only discover the isthmocele incidentally during imaging for other reasons.
Causes
Isthmocele develops due to incomplete healing or defective regeneration of the uterine wall after cesarean section. Contributing factors include:
- Surgical technique: Single-layer versus double-layer uterine closure, suture materials, and surgeon’s experience can influence healing.
- Infection or inflammation: Postoperative infections may impair scar formation.
- Poor blood supply: Reduced vascularization at the incision site affects tissue repair.
- Multiple cesarean sections: Repeated incisions increase the risk of defective healing.
- Timing between pregnancies: Short interpregnancy intervals may not allow adequate healing time.
- Patient factors: Smoking, diabetes, or conditions impairing wound healing.
- Uterine retroflexion: Anatomical position of the uterus may affect scar stress.
Risk Factors
- Previous cesarean delivery (primary risk factor).
- Multiple cesarean sections.
- Surgical technique and quality of uterine closure.
- Infection or postoperative complications.
- Short interval between cesarean and subsequent pregnancy.
- Poor nutritional or health status affecting healing.
- Uterine anomalies or retroflexed uterus.
Complications
If left untreated or undiagnosed, isthmocele can lead to several complications:
- Chronic abnormal uterine bleeding: Leading to anemia and reduced quality of life.
- Infertility: Due to altered uterine environment affecting implantation or sperm passage.
- Pelvic pain and discomfort: Impacting daily activities and sexual health.
- Increased risk of cesarean scar ectopic pregnancy: Rare but serious condition where implantation occurs in the scar niche.
- Uterine rupture: Especially during labor in subsequent pregnancies with a thin or weak scar.
- Adhesions or chronic inflammation: Can result from retained blood and secretions.
- Psychological impact: Due to chronic symptoms and fertility issues.
Prevention
While cesarean sections are sometimes necessary, strategies to reduce isthmocele risk include:
- Optimizing surgical techniques, such as meticulous multilayer uterine closure.
- Preventing and promptly treating postoperative infections.
- Allowing adequate interpregnancy intervals for uterine healing (usually at least 18-24 months).
- Managing patient health factors like diabetes and smoking cessation.
- Close monitoring in women with multiple cesarean deliveries.
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers a range of diagnostic and therapeutic options for managing isthmocele:
- Diagnosis:
- Transvaginal ultrasound is the primary imaging tool to identify the niche and assess its size and residual myometrial thickness.
- Sonohysterography (saline infusion sonography) provides enhanced visualization.
- MRI may be used for complex cases.
- Conservative management:
- Observation for asymptomatic cases.
- Hormonal therapy (oral contraceptives or progestins) to regulate bleeding and reduce spotting.
- Surgical treatments:
- Hysteroscopic resection: Minimally invasive removal or smoothing of the scar defect to improve bleeding and fertility outcomes.
- Laparoscopic repair: Surgical excision of the niche with reconstruction of the uterine wall, typically for larger or deeper defects or when hysteroscopy is not feasible.
- Vaginal repair: Less common but an option in select cases.
- These surgeries aim to restore normal uterine anatomy, reduce symptoms, and improve reproductive outcomes.
- Assisted reproductive technologies (ART): For women facing infertility linked to isthmocele, IVF and related treatments are available.
- Follow-up care: Regular monitoring with ultrasound and clinical assessment post-treatment.
- Research and integrative approaches: Korea also incorporates evidence-based complementary therapies to support reproductive health alongside conventional treatment.