Overview
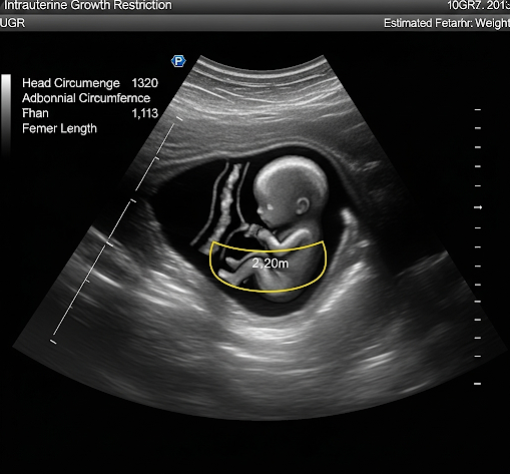
Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR), also known as fetal growth restriction, refers to a condition in which a fetus is smaller than expected for its gestational age, typically defined as an estimated fetal weight below the 10th percentile for the same gestational age. IUGR indicates that the fetus has not reached its genetically predetermined growth potential due to various maternal, placental, or fetal factors. It is a significant cause of perinatal morbidity and mortality worldwide. In Korea, advanced prenatal care including detailed ultrasound monitoring and fetal assessments allow early diagnosis and management of IUGR to improve neonatal outcomes.
What is Intrauterine Growth Restriction?
IUGR occurs when the fetus fails to grow at a normal rate inside the womb, often due to insufficient nutrient and oxygen supply. This impaired growth may affect the entire body or be asymmetric, with the head and brain relatively spared while the abdomen and limbs are disproportionately small.
IUGR is different from small-for-gestational-age (SGA) infants, who are small but otherwise healthy. IUGR specifically denotes pathological growth restriction and increased risk of complications.
Symptoms
Since the fetus is inside the uterus, symptoms are usually not directly noticed by the mother. However, clinical indicators and diagnostic findings include:
- Poor maternal weight gain during pregnancy.
- Decreased fetal movements reported by the mother.
- Discrepancy between uterine size and gestational age: The uterus measures smaller than expected.
- Ultrasound findings: Estimated fetal weight or abdominal circumference below the 10th percentile.
- Abnormal Doppler studies: Reduced blood flow in the umbilical artery or other fetal vessels.
Causes
IUGR can result from various maternal, placental, and fetal causes:
- Maternal factors:
- Chronic hypertension or preeclampsia.
- Diabetes mellitus (especially uncontrolled).
- Malnutrition or anemia.
- Smoking, alcohol, or drug abuse.
- Infections such as cytomegalovirus or toxoplasmosis.
- Advanced maternal age or multiple pregnancies.
- Placental factors:
- Placental insufficiency due to abnormal development or vascular disease.
- Placental abruption or previa.
- Umbilical cord abnormalities restricting blood flow.
- Fetal factors:
- Chromosomal abnormalities (e.g., trisomies).
- Congenital infections.
- Structural anomalies or genetic syndromes.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of IUGR:
- Maternal hypertension or preeclampsia.
- Smoking or substance abuse during pregnancy.
- Poor maternal nutrition or low body mass index.
- Previous history of IUGR or stillbirth.
- Multiple gestations (twins or higher order).
- Maternal infections during pregnancy.
- Placental abnormalities or insufficiency.
- Advanced maternal age (>35 years).
Complications
IUGR is associated with several adverse outcomes for both the fetus and newborn:
- Perinatal mortality: Increased risk of stillbirth or neonatal death.
- Preterm birth: Often delivered early to prevent further compromise.
- Hypoxia and acidosis: Due to poor placental blood flow.
- Low birth weight: Increases risk of hypothermia and infection.
- Neonatal complications: Respiratory distress, hypoglycemia, and difficulty feeding.
- Long-term effects: Increased risk of developmental delays, cerebral palsy, and chronic diseases such as hypertension, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease in adulthood.
Prevention
While not all cases of IUGR can be prevented, certain measures reduce risk:
- Adequate prenatal care: Early and regular check-ups to monitor fetal growth and maternal health.
- Healthy lifestyle: Balanced nutrition, avoidance of smoking, alcohol, and drugs.
- Management of maternal conditions: Control of hypertension, diabetes, and infections.
- Folic acid and vitamin supplementation.
- Monitoring high-risk pregnancies: Frequent ultrasounds and Doppler studies.
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers advanced prenatal care with a focus on early diagnosis and management of IUGR to optimize outcomes:
- Diagnostic Monitoring:
- Ultrasound: Regular fetal biometry to track growth parameters such as head circumference, abdominal circumference, and femur length.
- Doppler ultrasound: Assessment of blood flow in the umbilical artery, middle cerebral artery, and ductus venosus to detect fetal compromise.
- Non-stress tests (NST) and biophysical profiles (BPP): Evaluate fetal well-being.
- Management Strategies:
- Maternal health optimization: Treatment of hypertension, diabetes, or infections.
- Lifestyle counseling: Nutritional support and cessation of harmful substances.
- Close fetal surveillance: Frequent monitoring to detect signs of fetal distress.
- Timing of delivery: Early delivery may be necessary if fetal compromise worsens; decisions balance risks of prematurity against continued intrauterine stress.
- Hospitalization: In severe cases for intensive monitoring.
- Neonatal Care:
- Korean neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) are equipped to manage low birth weight and premature infants with advanced respiratory support and nutrition.
- Early intervention programs support long-term developmental outcomes.
- Multidisciplinary Approach:
- Coordination among obstetricians, maternal-fetal medicine specialists, neonatologists, nutritionists, and genetic counselors ensures comprehensive care.