Overview
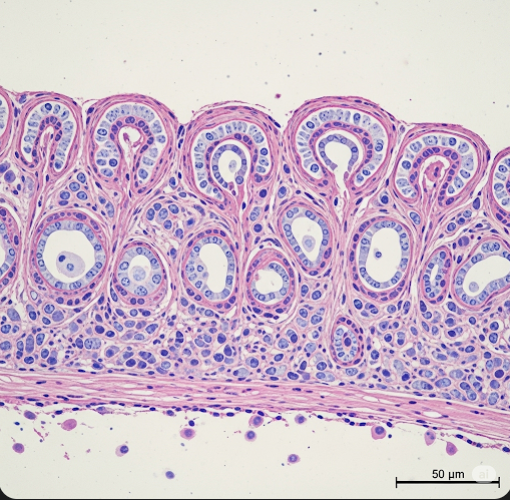
Intestinal metaplasia is a condition in which the normal lining cells of the stomach or esophagus are replaced by cells resembling those found in the intestines. This cellular transformation is considered a precancerous change because it increases the risk of developing gastric or esophageal cancer over time. In Korea, where gastric cancer rates are relatively high, early detection and management of intestinal metaplasia are key priorities in gastrointestinal healthcare. Korean medical centers employ advanced endoscopic techniques and careful monitoring strategies to manage this condition effectively.
What is Intestinal Metaplasia?
Intestinal metaplasia is a process where the epithelial cells lining the stomach or lower esophagus change their type to resemble the intestinal mucosa. This change is usually a response to chronic inflammation or injury, most commonly caused by Helicobacter pylori infection or chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
This metaplastic transformation involves replacing the normal gastric or esophageal cells with goblet cells and absorptive cells typical of the intestine. While the metaplasia itself is not cancer, it represents a step in the sequence of changes that can lead to dysplasia and eventually adenocarcinoma if left unchecked.
Symptoms
Intestinal metaplasia itself often does not cause symptoms and is typically detected during endoscopic examination for other digestive complaints. However, symptoms related to underlying causes or complications may include:
- Persistent indigestion or discomfort in the upper abdomen
- Chronic heartburn or acid reflux
- Nausea or bloating
- Unexplained weight loss in advanced cases
- Difficulty swallowing (if metaplasia affects the esophagus)
Because intestinal metaplasia is asymptomatic, regular screening in high-risk populations is essential for early diagnosis.
Causes
The primary causes of intestinal metaplasia include:
- Chronic Helicobacter pylori infection: The bacterium causes ongoing stomach inflammation leading to mucosal damage and metaplasia.
- Chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): Acid reflux irritates the esophageal lining, causing Barrett’s esophagus, a type of intestinal metaplasia.
- Smoking: Increases risk by promoting mucosal injury.
- Diet: High salt intake and diets low in fruits and vegetables may contribute.
- Age: The risk increases with advancing age due to prolonged exposure to irritants.
- Genetic predisposition: Some individuals may be more susceptible.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing intestinal metaplasia:
- Persistent Helicobacter pylori infection
- Long-standing GERD or Barrett’s esophagus
- Older age (above 50 years)
- Male gender: More common in men than women.
- Smoking and alcohol use
- Family history of gastric or esophageal cancer
- Dietary habits: High intake of smoked, salted, or pickled foods.
Complications
Intestinal metaplasia is a precancerous condition that can lead to:
- Dysplasia: Abnormal cell changes that can progress toward cancer.
- Gastric adenocarcinoma: The most common form of stomach cancer.
- Esophageal adenocarcinoma: Particularly in cases of Barrett’s esophagus.
- Ulceration and bleeding: Occasionally due to mucosal damage.
Early detection and surveillance are critical to prevent progression to cancer.
Prevention
Preventing intestinal metaplasia focuses on addressing its causes and risk factors:
- Eradication of Helicobacter pylori: Timely antibiotic treatment reduces inflammation and risk.
- Managing GERD: Use of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and lifestyle changes to reduce acid reflux.
- Healthy diet: Rich in fresh fruits, vegetables, and antioxidants; reduce salt and processed foods.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Regular medical check-ups: Particularly for high-risk individuals with chronic gastric or esophageal conditions.
- Weight management: Obesity is linked to GERD and Barrett’s esophagus.
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers advanced diagnostic and management options for intestinal metaplasia through specialized gastroenterology centers:
- Endoscopic Surveillance:
Regular endoscopic exams with biopsy are standard to monitor the extent of intestinal metaplasia and detect any progression to dysplasia or cancer. Korea utilizes high-definition endoscopy and chromoendoscopy to enhance visualization. - Helicobacter pylori Eradication:
Korean physicians prescribe effective antibiotic regimens to eliminate H. pylori infection, significantly lowering the risk of progression. - Medical Therapy:
Use of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) to control acid reflux and promote mucosal healing in cases associated with GERD. - Lifestyle and Dietary Counseling:
Korean healthcare providers emphasize patient education on diet, smoking cessation, and weight control. - Endoscopic Treatments:
In cases where dysplasia or early cancer develops, minimally invasive procedures like endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) or endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) are available and widely practiced in Korea to remove abnormal tissue. - Multidisciplinary Care:
Gastroenterologists, pathologists, and oncologists collaborate closely to tailor follow-up and treatment plans. - Research and Clinical Trials:
Korea actively contributes to global research on gastric and esophageal precancerous conditions, providing patients access to innovative therapies.