Overview
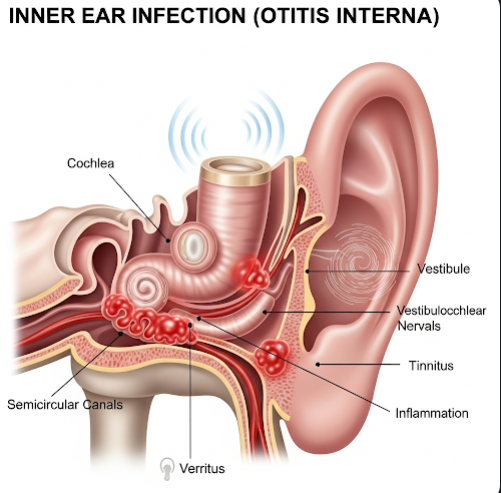
An inner ear infection, medically known as Otitis Interna or Labyrinthitis, is a condition where the innermost part of the ear becomes inflamed due to infection, injury, or autoimmune disorders. The inner ear contains the cochlea (for hearing) and the vestibular system (for balance). When these delicate structures are affected, patients can experience hearing loss, dizziness, and balance problems.
In Korea, otitis interna is diagnosed and treated using advanced ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat) medical technology, including high-resolution imaging, audiometric testing, and minimally invasive procedures. Korean healthcare facilities also emphasize quick intervention to prevent long-term hearing or balance damage.
What is Inner Ear Infection (Otitis Interna)?
Otitis interna is an inflammation of the labyrinth—a complex structure in the inner ear made up of fluid-filled channels and delicate sensory cells. The infection can be viral (most common), bacterial, or caused by other medical conditions that affect the inner ear.
While ear infections in the outer or middle ear are relatively common, inner ear infections are less frequent but often more serious. They can lead to permanent hearing loss or chronic balance problems if not treated promptly.
Symptoms
The symptoms of otitis interna can appear suddenly and vary in intensity, but they often include:
- Sudden hearing loss in one or both ears
- Vertigo (a spinning sensation)
- Loss of balance or unsteadiness when walking
- Tinnitus (ringing or buzzing in the ear)
- Nausea and vomiting due to severe dizziness
- Pressure or fullness in the ear
- Difficulty focusing vision (oscillopsia) in severe cases
These symptoms can be temporary if treated early, but delayed treatment may cause permanent issues.
Causes
Otitis interna can be caused by various factors, including:
- Viral infections such as influenza, herpes simplex virus, or measles
- Bacterial infections spreading from untreated middle ear infections (otitis media)
- Autoimmune inner ear disease where the body’s immune system attacks inner ear tissues
- Head trauma damaging the labyrinth
- Vascular disorders affecting blood supply to the inner ear
- Chronic inflammatory diseases such as meningitis or syphilis affecting the ear structures
Risk Factors
The likelihood of developing otitis interna increases with certain factors:
- Having a recent upper respiratory infection (cold or flu)
- Chronic middle ear infections
- Weak immune system
- Autoimmune diseases
- History of severe allergies or sinus infections
- Smoking, which can impair immune defense in ear tissues
- Prolonged exposure to loud noises (indirectly affecting ear health)
Complications
If left untreated, otitis interna can lead to severe and sometimes irreversible complications, including:
- Permanent sensorineural hearing loss
- Chronic vertigo and balance disorders
- Spread of infection to surrounding tissues, including the brain (meningitis)
- Anxiety and depression due to persistent symptoms
- Difficulty performing daily activities due to dizziness or hearing loss
Prevention
While not all cases can be prevented, the risk can be reduced with the following measures:
- Treat colds, flu, and sinus infections promptly
- Get vaccinated against viruses like influenza and measles
- Avoid smoking and secondhand smoke
- Protect ears from water contamination (especially in swimming pools or polluted water)
- Manage allergies and sinus problems early
- Maintain good hygiene to reduce infection risks
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Korean ENT specialists use a combination of patient history, physical examination, and advanced diagnostic tools such as:
- Audiometry to assess hearing loss
- Vestibular tests (ENG/VNG) to measure balance function
- MRI or CT scans to detect inflammation or structural issues in the inner ear
- Blood tests to check for infections or autoimmune markers
Medical Treatment
- Antiviral or antibiotic therapy depending on the underlying cause
- Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and swelling in the inner ear
- Vestibular suppressants such as meclizine or diazepam to control vertigo
- Anti-nausea medications to relieve vomiting and dizziness
- Intratympanic steroid injections in severe cases for direct medication delivery
Rehabilitation
For patients with prolonged balance issues, vestibular rehabilitation therapy (VRT) is widely available in Korea. This specialized physiotherapy retrains the brain to adapt to balance changes.
Surgical Options
In rare cases where infection causes abscesses or severe damage, surgery such as labyrinthectomy or drainage may be performed. Korean hospitals are equipped with minimally invasive techniques to reduce recovery time.
Prognosis in Korea
Early detection and treatment significantly improve recovery outcomes. Many patients treated in Korean medical centers regain full hearing and balance function, especially if therapy begins within the first 72 hours of symptom onset.