Overview
An inguinal hernia in babies is a common condition where a part of the intestine or abdominal tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the lower abdominal wall, specifically in the inguinal canal located in the groin area. This condition occurs due to incomplete closure of the inguinal canal during fetal development. Inguinal hernias are particularly common in premature infants and boys. In Korea, pediatric surgeons use advanced diagnostic and surgical techniques to safely repair inguinal hernias in babies, ensuring quick recovery and minimal complications.
What is an Inguinal Hernia in Babies?
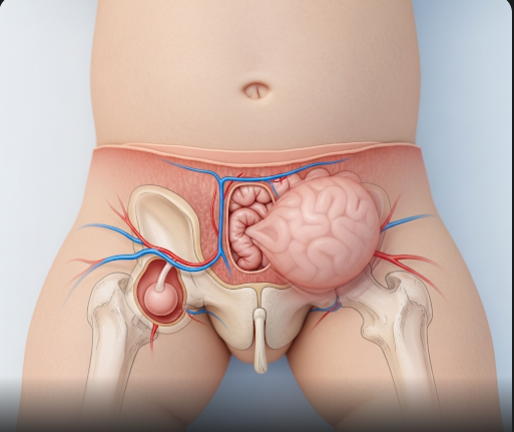
An inguinal hernia happens when tissue, such as part of the intestine, pushes through a weakness in the abdominal muscles near the groin. In babies, this often occurs because the inguinal canal—a passageway that allows structures like the spermatic cord in boys or the round ligament in girls to pass from the abdomen to the groin—does not close completely after birth. This leaves an opening that allows abdominal contents to bulge out, creating a visible lump in the groin or scrotum.
Symptoms
- A noticeable soft lump or bulge in the groin or scrotal area, especially when crying, coughing, or straining
- The lump may disappear or reduce when the baby is calm or lying down
- Irritability or discomfort in the baby, especially if the hernia becomes trapped (incarcerated)
- Swelling or tenderness in the groin or scrotum
- Vomiting, abdominal pain, or signs of distress if the hernia is strangulated (blood supply is cut off) — this is a medical emergency
Causes
- Incomplete closure of the inguinal canal after birth
- Prematurity, which increases the risk due to underdeveloped abdominal muscles
- Increased intra-abdominal pressure from crying, straining, or constipation
- Family history may play a role
Risk Factors
- Premature birth
- Male gender, as the inguinal canal is larger in boys due to testicular descent
- Low birth weight
- Conditions that increase abdominal pressure such as chronic coughing or constipation
Complications
- Incarceration: When the herniated tissue becomes trapped and cannot be pushed back in, leading to pain and swelling.
- Strangulation: A severe complication where blood supply to the trapped intestine is cut off, causing tissue death. This is a surgical emergency requiring immediate attention.
- Bowel obstruction leading to vomiting and abdominal distension
Prevention
- There is no known way to prevent congenital inguinal hernias in babies as they are related to developmental factors.
- Prompt medical evaluation of any groin swelling in infants is essential.
- Avoid delaying treatment once diagnosed to prevent complications.
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Physical examination by a pediatric surgeon, often sufficient for diagnosis
- Ultrasound imaging may be used to confirm the diagnosis or assess complications
Medical Treatments
- There is no effective non-surgical treatment for inguinal hernias in babies; observation is only acceptable in very rare cases without symptoms.
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Herniorrhaphy: The standard treatment involves surgery to push the protruding tissue back into the abdomen and close the opening in the abdominal wall.
- The procedure is often done under general anesthesia with minimally invasive laparoscopic techniques increasingly common in Korea.
- Surgery is typically recommended soon after diagnosis to avoid the risk of incarceration or strangulation.
Rehabilitation and Support
- Most babies recover quickly and can resume normal feeding and activities within a day or two after surgery.
- Postoperative monitoring to watch for signs of infection or recurrence is essential.
- Parents receive guidance on wound care and activity restrictions during recovery.
Top Hospitals or Clinics in Korea
- Seoul National University Children’s Hospital – Pediatric Surgery Department
- Samsung Medical Center – Pediatric Surgery and Minimally Invasive Surgery Center
- Asan Medical Center – Children’s Hospital Surgical Unit
- Yonsei Severance Children’s Hospital – Pediatric Surgery Clinic