Overview
Ingrown hairs are a common dermatological condition where hair curls back or grows sideways into the skin instead of emerging outward. This leads to inflammation, irritation, and sometimes infection. While ingrown hairs can occur anywhere on the body where hair grows, they are most commonly seen in areas that undergo frequent shaving or waxing, such as the beard, legs, and bikini line. In Korea, dermatologists offer a range of treatment options, from topical therapies to laser hair removal, to effectively manage and prevent ingrown hairs and associated complications.
What Is an Ingrown Hair?
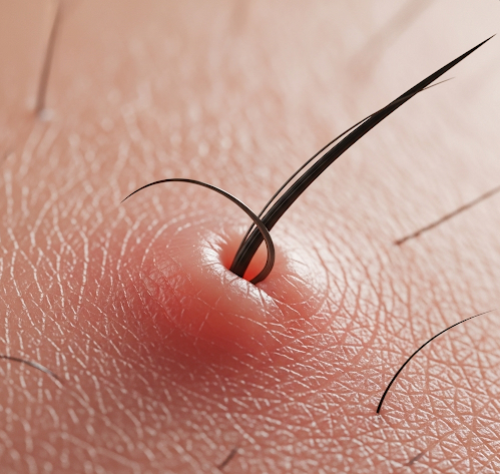
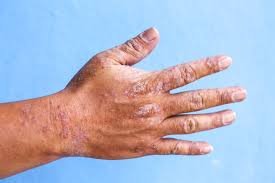
An ingrown hair occurs when a hair follicle becomes trapped beneath the skin’s surface or grows sideways into the surrounding skin, causing irritation and a localized inflammatory reaction. The condition is often a result of hair removal methods like shaving, waxing, or plucking, which can damage the hair follicle or cause hair to regrow improperly. Ingrown hairs can cause bumps, redness, and sometimes pus-filled lesions, resembling acne or folliculitis.
Symptoms
- Small, raised bumps that may be red or skin-colored
- Itching or tenderness around the affected area
- Inflammation and swelling
- Presence of pus-filled blisters or pustules if infection occurs
- Darkening of the skin (hyperpigmentation) in chronic cases
- Pain or discomfort, especially if irritated or infected
Causes
- Shaving, waxing, or plucking hairs, which may cut hair at an angle that favors inward growth
- Curly or coarse hair types, which are more prone to curling back into the skin
- Wearing tight clothing that irritates hair follicles
- Dead skin cells clogging hair follicles, trapping hairs beneath the skin
- Improper shaving techniques or dull razors
- Certain skin conditions such as folliculitis
Risk Factors
- Individuals with naturally curly or coarse hair
- Frequent shaving or other hair removal methods
- Use of blunt or poor-quality razors
- Poor exfoliation or skin hygiene
- Wearing tight clothing or friction-inducing garments
- Hormonal changes that increase hair growth
Complications
- Secondary bacterial infection leading to folliculitis or abscess formation
- Scarring or permanent skin discoloration (post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation)
- Formation of keloids in susceptible individuals
- Chronic irritation and discomfort affecting daily activities
Prevention
- Using proper shaving techniques such as shaving in the direction of hair growth
- Keeping skin moisturized and exfoliated regularly to prevent clogged follicles
- Using sharp, clean razors or considering alternative hair removal methods like depilatory creams or laser therapy
- Avoiding tight clothing that causes friction in hair-prone areas
- Applying soothing aftershave products containing ingredients like aloe vera or salicylic acid
- Consulting a dermatologist for persistent or severe cases
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean dermatologists provide a comprehensive range of treatments to manage and prevent ingrown hairs:
- Topical Therapies:
- Antibiotic creams for infected lesions
- Corticosteroid creams to reduce inflammation
- Retinoids to promote exfoliation and prevent follicle blockage
- Physical Removal:
- Careful extraction of ingrown hairs under sterile conditions
- Laser Hair Removal:
- Permanent reduction of hair growth in affected areas using laser technology, reducing the risk of recurrence
- Professional Skin Care:
- Regular exfoliation and moisturizing treatments at dermatology clinics
- Guidance on proper shaving and skin care techniques
- Preventive Advice:
- Patient education on hair removal methods and skin hygiene to avoid future ingrown hairs
Korea’s advanced cosmetic dermatology sector combines medical treatments with aesthetic care to offer effective and lasting solutions for ingrown hairs, improving both skin health and appearance.