Overview
Infertility is a common reproductive health condition defined as the inability to conceive after one year of regular, unprotected intercourse. It affects millions of couples worldwide and has multifactorial causes involving both partners. In Korea, advancements in diagnostic technologies, assisted reproductive techniques, and holistic approaches have made infertility treatment more accessible and successful. Addressing infertility early and comprehensively improves the chances of conception and helps couples achieve their family-building goals.
What Is Infertility?
Infertility refers to the failure to achieve pregnancy after 12 months of regular, unprotected sexual intercourse. It can be classified as primary infertility (when a couple has never conceived) or secondary infertility (difficulty conceiving after a previous pregnancy). Both male and female factors can contribute, and sometimes the cause remains unexplained.
Symptoms
- Inability to conceive despite regular intercourse
- Irregular or absent menstrual cycles in women
- Painful periods or pelvic pain
- Recurrent miscarriages or pregnancy losses
- In men, signs of hormonal imbalance such as decreased libido or erectile dysfunction
- No obvious symptoms in some cases; infertility is often identified during fertility evaluations
Causes
Infertility can arise from a variety of factors affecting reproductive anatomy, function, or hormonal balance:
In Women:
- Ovulatory disorders such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Tubal blockage or damage from infections or surgeries
- Endometriosis causing inflammation and scarring
- Uterine abnormalities like fibroids or polyps
- Age-related decline in egg quality and quantity
- Hormonal imbalances affecting ovulation
In Men:
- Low sperm count or poor sperm motility
- Varicocele (enlargement of veins in the scrotum)
- Hormonal imbalances
- Genetic disorders affecting sperm production
- Exposure to toxins or environmental hazards
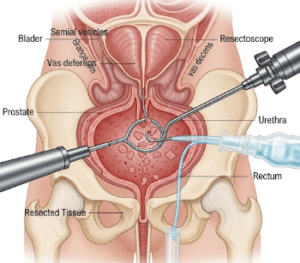
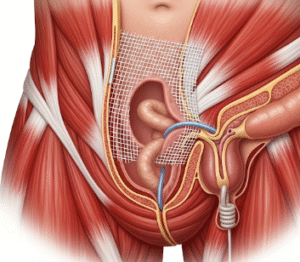
- Structural abnormalities such as blockage of the vas deferens
Both partners:
- Unexplained infertility where no clear cause is found
- Lifestyle factors such as smoking, obesity, stress, and excessive alcohol use
Risk Factors
- Advanced maternal age (especially over 35)
- History of pelvic infections or sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- Chronic medical conditions such as diabetes or thyroid disorders
- Excessive physical or emotional stress
- Exposure to environmental toxins and radiation
- Obesity or significant underweight
- Repeated use of certain medications or substances
Complications
- Emotional distress, anxiety, and depression related to difficulty conceiving
- Strain on personal relationships and social isolation
- Financial burden from fertility treatments
- Possible health risks associated with assisted reproductive technologies (ART)
- Risk of multiple pregnancies and associated complications from fertility treatments
Prevention
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with balanced diet and regular exercise
- Avoiding smoking, excessive alcohol, and illicit drugs
- Managing chronic health conditions effectively
- Practicing safe sex to prevent infections
- Seeking timely medical advice if conception does not occur within one year
- Minimizing exposure to environmental toxins
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea is recognized for its advanced fertility clinics and integrated reproductive health services offering a wide spectrum of treatments:
- Diagnostic Evaluations:
- Hormonal profiling, ultrasound, hysterosalpingography, and semen analysis
- Genetic testing and laparoscopic evaluation if needed
- Medical Treatments:
- Ovulation induction with medications such as clomiphene citrate or gonadotropins
- Treatment of infections or hormonal imbalances
- Surgery for structural abnormalities such as fibroid removal or tubal surgery
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART):
- Intrauterine insemination (IUI) for mild cases
- In vitro fertilization (IVF) and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) for more complex cases
- Preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) for genetic disorders
- Cryopreservation of eggs, sperm, or embryos
- Complementary and Supportive Care:
- Counseling and psychological support
- Nutritional guidance and lifestyle coaching
- Traditional Korean medicine and acupuncture as adjunct therapies
Korean fertility centers emphasize personalized care plans combining the latest medical advances with emotional support, aiming to maximize success rates and patient satisfaction.