Overview
Infected ear piercing is a frequent complication resulting from the introduction of bacteria or other pathogens into the pierced skin site. Ear piercing is a popular cosmetic practice globally, including Korea, often performed for cultural, aesthetic, or personal reasons. While generally safe when done professionally, infections can occur due to improper technique, poor aftercare, or use of unsterile equipment. Early recognition and appropriate treatment are vital to prevent serious complications like abscesses, scarring, or systemic infections.
What is Infected Ear Piercing?
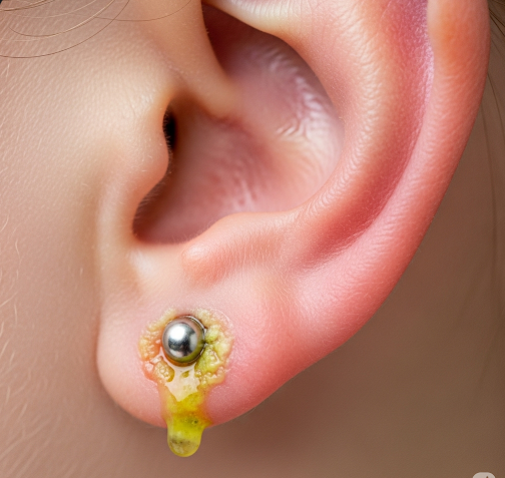
Infected ear piercing refers to the inflammation and infection that develops around a pierced site, usually caused by bacterial contamination. The infection typically manifests soon after the piercing procedure but can also develop later due to inadequate hygiene or irritation. The infection may affect the skin and soft tissues around the piercing and sometimes extend to the cartilage if the piercing is done on the upper ear.
Symptoms
The clinical presentation of infected ear piercing can vary from mild irritation to severe inflammation. Common symptoms include:
- Redness and swelling: The area around the piercing becomes noticeably red, swollen, and warm to the touch.
- Pain and tenderness: The site often becomes painful or tender, especially when touched or moved.
- Discharge: Pus or yellowish fluid may ooze from the piercing, indicating bacterial infection.
- Itching or burning sensation: The area may feel itchy or have a burning discomfort.
- Crusting or scabbing: Dried discharge can form a crust or scab around the piercing.
- Fever or swollen lymph nodes: In more severe infections, systemic symptoms like fever or swelling of lymph nodes near the ear may occur.
- Delayed healing: The piercing site may fail to heal or worsen over time.
Causes
The primary cause of infection is bacterial colonization, most commonly by Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus species, or Pseudomonas aeruginosa in moist environments. Other contributing factors include:
- Non-sterile piercing techniques: Use of contaminated needles or unsterilized equipment during the piercing process.
- Poor aftercare: Failure to clean the piercing regularly or touching it with unwashed hands.
- Allergic reactions: Sensitivity or allergy to certain metals in earrings, such as nickel, can cause irritation that predisposes to infection.
- Excessive manipulation: Twisting or playing with earrings can disrupt the healing tissue and introduce bacteria.
- Skin conditions: Pre-existing skin diseases like eczema or dermatitis increase vulnerability to infections.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing an infected ear piercing:
- Piercing by untrained personnel: In non-professional settings without adequate hygiene standards.
- Delay in cleaning: Not following recommended aftercare routines.
- Use of low-quality jewelry: Earrings made from cheap metals that irritate the skin.
- Immune suppression: Conditions or medications that impair immune defenses.
- Age and skin type: Younger children or those with sensitive skin may be more prone.
Complications
If untreated or improperly managed, infected ear piercings can lead to:
- Abscess formation: A localized collection of pus requiring drainage.
- Keloid or hypertrophic scars: Overgrowth of scar tissue causing cosmetic deformity.
- Cellulitis: Infection spreading to surrounding skin and soft tissue, potentially requiring systemic antibiotics.
- Cartilage infection (perichondritis): Particularly in piercings through the ear cartilage, which can cause permanent deformity.
- Systemic infection: Rare but serious bloodstream infections may occur, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
Prevention
Preventing infected ear piercing involves:
- Choosing professional studios: Ensure piercings are done by trained personnel using sterile techniques.
- Sterilization of equipment: Needles and instruments should be single-use or properly sterilized.
- Proper aftercare: Cleaning the site daily with recommended antiseptic solutions and avoiding unnecessary touching.
- Using hypoallergenic jewelry: Prefer gold, surgical steel, or titanium earrings to minimize allergic reactions.
- Avoiding swimming or exposure to dirty water: Until the piercing is fully healed.
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Healthcare providers diagnose infected ear piercing primarily through clinical examination, noting redness, swelling, and discharge. In persistent or severe cases, swabs may be taken for culture and sensitivity testing to guide antibiotic therapy.
Medical Treatments
- Topical antibiotics: For mild infections, antibiotic ointments such as mupirocin or fusidic acid can be effective.
- Oral antibiotics: In moderate to severe cases, oral antibiotics targeting common skin bacteria are prescribed.
- Pain relief: Over-the-counter analgesics help manage discomfort.
- Warm compresses: Applying warm compresses can promote drainage and reduce inflammation.
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Incision and drainage: Required for abscess formation to remove pus and prevent spread.
- Earring removal: If infection does not resolve or worsens, removal of earrings may be necessary to allow healing.
Rehabilitation and Support
- Follow-up care: Regular check-ups to ensure resolution of infection and healing.
- Scar treatment: Dermatological procedures for hypertrophic scars or keloids, such as corticosteroid injections or laser therapy.
- Patient education: Guidance on hygiene and aftercare to prevent recurrence.
Top Hospitals or Clinics in Korea
- Seoul National University Hospital – Dermatology and Infectious Diseases Departments
- Samsung Medical Center – Skin and Soft Tissue Infection Clinic
- Asan Medical Center – Department of Dermatology
- Yonsei Severance Hospital – Dermatology and Minor Surgery Unit