Overview
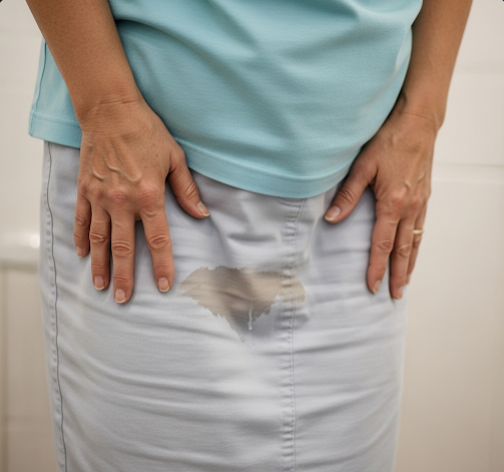
Urinary incontinence is the involuntary leakage of urine, a common condition that affects millions worldwide, including people of all ages and genders. It can range from occasional minor leaks to complete loss of bladder control, significantly impacting quality of life. In Korea, urology and gynecology specialists provide comprehensive evaluation and a variety of treatment options tailored to the type and severity of urinary incontinence, helping patients regain control and improve daily functioning.
What Is Urinary Incontinence?
Urinary incontinence refers to any involuntary loss of urine. It results from problems in the bladder, urethra, or nervous system that disrupt normal storage and release of urine. The condition can be transient or chronic, temporary or permanent, and is classified into different types depending on the underlying cause and symptoms, such as stress incontinence, urge incontinence, overflow incontinence, and functional incontinence.
Symptoms
- Leakage of urine during activities that increase abdominal pressure (e.g., coughing, sneezing, lifting) – typical of stress incontinence
- Sudden, intense urge to urinate followed by involuntary leakage – characteristic of urge incontinence
- Constant dribbling of urine due to incomplete bladder emptying – overflow incontinence
- Difficulty reaching the bathroom in time due to physical or cognitive impairments – functional incontinence
- Frequent urination or nocturia (waking at night to urinate) may accompany some types
Causes
Urinary incontinence can arise from various factors affecting bladder function or the urinary tract:
- Weakness or damage to pelvic floor muscles or sphincters
- Overactive bladder muscles causing urgency and frequency
- Neurological disorders such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, or spinal cord injury
- Urinary tract infections causing temporary incontinence
- Prostate enlargement in men obstructing urine flow
- Certain medications and lifestyle factors (e.g., caffeine, alcohol)
Risk Factors
- Aging and menopause in women causing hormonal and muscle changes
- Pregnancy, childbirth, and pelvic surgeries weakening pelvic muscles
- Obesity increasing abdominal pressure on the bladder
- Chronic coughing (from smoking or respiratory diseases)
- Neurological diseases and injuries affecting bladder control
- Diabetes causing nerve damage
- Sedentary lifestyle and poor physical fitness
Complications
- Skin irritation and infections from constant moisture exposure
- Social embarrassment and isolation
- Sleep disturbances and fatigue due to nocturia
- Reduced participation in work, exercise, and social activities
- Psychological distress, including anxiety and depression
Prevention
- Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise
- Performing pelvic floor muscle exercises (Kegel exercises) regularly
- Managing chronic conditions such as diabetes and respiratory diseases
- Avoiding bladder irritants like caffeine and alcohol
- Timely treatment of urinary tract infections
- Practicing good toileting habits and avoiding constipation
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean healthcare providers use a personalized, multidisciplinary approach to manage urinary incontinence effectively:
- Behavioral Therapies:
- Bladder training to increase bladder capacity and control urgency
- Pelvic floor muscle exercises guided by physiotherapists
- Lifestyle modifications including fluid management and dietary changes
- Medications:
- Anticholinergics or beta-3 agonists to relax overactive bladder muscles
- Topical estrogen therapy for postmenopausal women to strengthen urethral tissues
- Medications to address underlying conditions contributing to incontinence
- Medical Devices and Procedures:
- Use of pessaries in women to support pelvic organs
- Electrical stimulation or biofeedback for pelvic muscle strengthening
- Minimally invasive procedures like urethral bulking injections
- Surgical Treatments:
- Sling procedures or bladder neck suspension for stress incontinence
- Neuromodulation therapy for refractory urge incontinence
- Prostate surgery for men with obstruction-related incontinence
- Supportive Care:
- Continence products such as pads or catheters when needed
- Psychological counseling to address emotional impacts
Korea’s advanced urology and gynecology centers integrate the latest technologies with holistic care models to restore bladder control and improve patient quality of life.