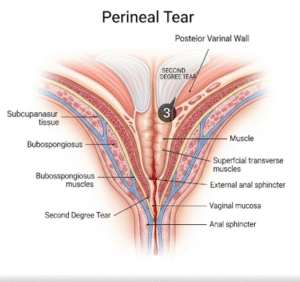
Overview
Incontinence refers to the involuntary loss of control over bodily functions, most commonly involving urine or feces. It is a prevalent condition that affects people across all ages but is especially common among older adults and individuals with certain medical conditions. Incontinence can significantly impact physical health, emotional wellbeing, and social life, making it an important health concern worldwide. In Korea, a multidisciplinary healthcare system offers a wide range of diagnostic, therapeutic, and supportive care options to manage incontinence effectively and improve patients’ quality of life.
What Is Incontinence?
Incontinence broadly describes the inability to control the release of urine or feces voluntarily. It is generally categorized into two main types:
- Urinary Incontinence: The involuntary leakage of urine due to dysfunction of the bladder, urethra, or nervous system.
- Fecal (or Anal) Incontinence: The inability to control bowel movements, leading to unintentional passage of stool.
Both types can vary from occasional minor leakage to complete loss of control and may result from different underlying causes.
Symptoms
- Urinary incontinence symptoms include:
- Leakage of urine with coughing, sneezing, or physical exertion (stress incontinence)
- Sudden urge to urinate followed by leakage (urge incontinence)
- Constant dribbling or overflow of urine
- Frequent urination or nocturia
- Fecal incontinence symptoms include:
- Involuntary passage of stool or gas
- Difficulty controlling bowel movements
- Leakage of mucus or liquid stool
- Urgency and inability to reach the bathroom in time
Causes
Incontinence can be caused by a wide range of factors affecting muscles, nerves, or structures involved in bladder or bowel control:
- Weakening or injury to pelvic floor muscles or sphincters
- Neurological disorders such as stroke, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury, or dementia
- Chronic constipation or diarrhea affecting bowel control
- Urinary tract infections
- Prostate problems in men
- Pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause-related changes in women
- Medications affecting bladder or bowel function
- Surgery or trauma to pelvic organs
Risk Factors
- Advanced age, as muscle tone and nerve function decline
- Female gender due to childbirth and hormonal changes
- Obesity, which increases abdominal pressure
- Chronic respiratory diseases causing coughing
- Diabetes and other chronic illnesses
- Sedentary lifestyle and poor nutrition
- Previous pelvic or abdominal surgeries
Complications
- Skin irritation, infections, and sores due to constant moisture exposure
- Sleep disturbances and fatigue
- Social withdrawal, embarrassment, and reduced self-esteem
- Depression and anxiety due to chronic symptoms
- Reduced participation in daily activities and work
Prevention
- Maintaining a healthy weight and balanced diet
- Regular physical activity to strengthen pelvic muscles
- Avoiding bladder and bowel irritants like caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods
- Practicing pelvic floor exercises (Kegel exercises)
- Timely management of urinary or bowel infections
- Proper management of chronic diseases
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers comprehensive and integrated care for incontinence, including:
- Behavioral Interventions:
- Bladder and bowel training programs
- Lifestyle and dietary modifications
- Pelvic floor muscle rehabilitation through physiotherapy
- Medications:
- Drugs to reduce bladder overactivity or improve sphincter function
- Treatments targeting bowel motility and stool consistency
- Medical Devices and Procedures:
- Use of pessaries or urethral inserts
- Electrical stimulation and biofeedback therapy
- Minimally invasive interventions such as botulinum toxin injections
- Surgical Treatments:
- Sling surgeries and bladder neck suspensions for urinary incontinence
- Sphincter repair or artificial sphincter implantation for fecal incontinence
- Neuromodulation therapies for refractory cases
- Supportive and Palliative Care:
- Continence products including pads, catheters, and absorbent garments
- Psychological support and counseling
- Community and caregiver education
Korea’s healthcare system integrates modern technology with patient-centered care to address the physical, emotional, and social aspects of incontinence, improving outcomes and quality of life.