Overview
An incarcerated hernia is a serious medical condition where a portion of the intestine or abdominal tissue becomes trapped (incarcerated) in a hernia sac and cannot be pushed back into the abdomen. This leads to compromised blood flow, causing swelling and pain, and may progress to strangulation, which is a surgical emergency. In Korea, hospitals and surgical centers specialize in prompt diagnosis and advanced minimally invasive surgery to treat incarcerated hernias effectively and prevent complications.
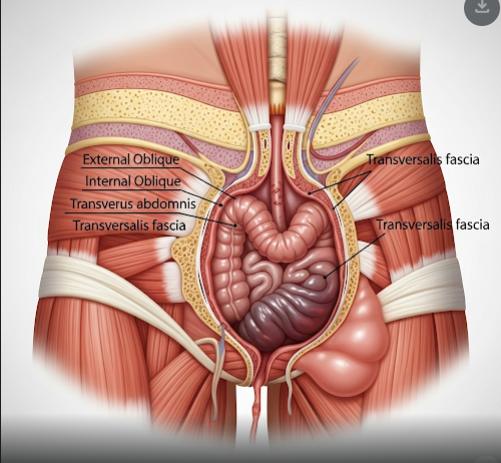
What is an Incarcerated Hernia?
A hernia occurs when an internal organ or tissue pushes through a weak spot in the abdominal wall. When this herniated tissue becomes stuck and cannot be reduced back into the abdomen, it is termed an incarcerated hernia. This condition can cause bowel obstruction and, if untreated, may lead to tissue death (strangulation).
Symptoms
- Sudden, severe pain at the hernia site
- A tender, firm, and swollen bulge that cannot be pushed back
- Nausea and vomiting, especially if bowel obstruction occurs
- Redness or discoloration over the hernia area
- Fever and signs of systemic infection in advanced cases
- Constipation or inability to pass gas
Causes
- Weakness in the abdominal muscles or connective tissue
- Heavy lifting, straining, or increased intra-abdominal pressure
- Previous hernia repair with recurrence
- Trauma or surgical incisions
Risk Factors
- Males are more commonly affected, especially for inguinal hernias
- Obesity and chronic coughing
- Pregnancy and aging
- Chronic constipation or urinary obstruction increasing abdominal pressure
Complications
- Strangulated hernia causing ischemia and necrosis of trapped tissue
- Bowel obstruction leading to severe abdominal symptoms
- Infection and sepsis if tissue perforates or dies
- Emergency surgery with increased risks and longer recovery
Prevention
- Avoid heavy lifting or sudden strain
- Maintain healthy weight and manage chronic cough or constipation
- Early treatment of small or reducible hernias before incarceration occurs
- Regular medical follow-up for known hernias
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Physical examination detecting a tender, irreducible bulge
- Ultrasound or CT scan to assess hernia contents and complications
- Blood tests if infection or systemic illness is suspected
Medical Treatments
- Emergency hospitalization for pain management and stabilization
- Nasogastric decompression in bowel obstruction cases
- Intravenous fluids and antibiotics if infection is present
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Prompt surgical intervention is essential to relieve incarceration
- Laparoscopic or open hernia repair techniques depending on case specifics
- Resection of necrotic bowel if strangulation has occurred
- Use of mesh reinforcement to reduce recurrence
Rehabilitation and Support
- Postoperative pain control and wound care
- Early mobilization to prevent complications like blood clots
- Dietary adjustments and gradual return to activities
- Follow-up to monitor healing and detect recurrence
Top Hospitals or Clinics in Korea
- Seoul National University Hospital – Department of General Surgery
- Samsung Medical Center – Hernia and Minimally Invasive Surgery Clinic
- Asan Medical Center – Abdominal Surgery Unit
- Yonsei Severance Hospital – Digestive Surgery Department