Overview
Imperforate hymen is a congenital condition where the hymen, a thin membrane partially covering the vaginal opening, completely obstructs the vaginal entrance. This condition occurs during fetal development when the hymen fails to perforate, preventing normal menstrual flow and causing various symptoms. In Korea, pediatric gynecology and urology specialists diagnose and treat imperforate hymen through non-invasive exams and minor surgical procedures, ensuring normal reproductive health and relieving symptoms.
What is Imperforate Hymen?
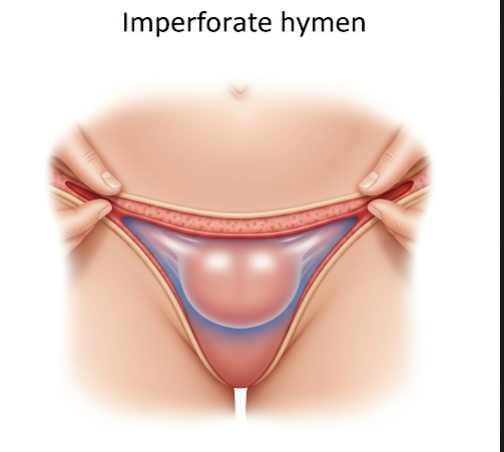
Imperforate hymen is a birth defect where the hymenal membrane completely covers the vaginal opening, leaving no opening for menstrual blood or vaginal secretions to exit. It is usually diagnosed during adolescence when menstrual periods begin but cannot pass through the blocked hymen, leading to symptoms.
Symptoms
- Absence of menstruation (primary amenorrhea) despite normal development
- Cyclical pelvic or lower abdominal pain due to trapped menstrual blood (hematocolpos)
- Bulging or bluish swelling at the vaginal opening
- Urinary retention or difficulty urinating in some cases
- Back pain or constipation caused by pressure from accumulated blood
- In rare newborn cases, vaginal swelling or mucus discharge
Causes
- Failure of hymenal membrane to perforate during fetal development
- Genetic or developmental anomalies affecting vaginal canal formation
Risk Factors
- Congenital anomaly present at birth (no specific risk factors identified)
- Family history of reproductive tract malformations (rare)
Complications
- Pain and discomfort from blood accumulation behind the hymen
- Urinary retention leading to bladder issues
- Infection risk if menstrual blood remains trapped
- Potential impact on fertility if untreated for extended periods
Prevention
- Not preventable due to congenital origin
- Early diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Physical examination revealing bulging hymenal membrane
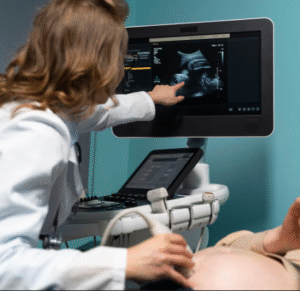
- Ultrasound imaging to detect fluid accumulation in the vagina and uterus
- MRI in complex or unclear cases to assess anatomy
Medical Treatments
- None; treatment is primarily surgical
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Hymenotomy or hymenectomy: a minor surgical procedure to create an opening in the hymen
- Drainage of accumulated menstrual blood during surgery if necessary
- Minimally invasive approaches to minimize scarring and preserve normal anatomy
Rehabilitation and Support
- Postoperative care including hygiene instructions and pain management
- Follow-up visits to monitor healing and menstrual flow
- Counseling and education for patients and families about normal reproductive health
Top Hospitals or Clinics in Korea
- Seoul National University Hospital – Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Asan Medical Center – Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology
- Samsung Medical Center – Women’s Health Clinic
- Yonsei Severance Hospital – Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology