Overview
Genital herpes is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), primarily HSV-2 but sometimes HSV-1. In Korea, awareness and treatment options are improving, though stigma can delay diagnosis. Early detection and antiviral therapy are essential to manage symptoms and prevent transmission.
What is Herpes (Genital)?
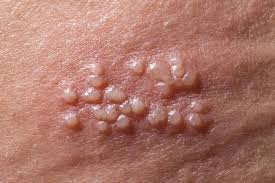
Genital herpes is a viral infection that causes recurrent sores and blisters in the genital and anal areas. It is highly contagious and transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Both men and women can be affected, and the infection can persist lifelong with periodic flare-ups.
Symptoms
- Painful blisters or sores on the genital or anal area
- Itching or burning sensation before sores appear
- Pain during urination
- Flu-like symptoms such as fever, muscle aches, or swollen lymph nodes (especially during the first outbreak)
- Recurrent outbreaks that are milder and shorter than the initial episode
Causes
- Infection with herpes simplex virus (HSV-1 or HSV-2)
- Direct skin-to-skin or mucous membrane contact with an infected person, often during sexual activity
- Viral reactivation triggered by stress, illness, or a weakened immune system
Risk Factors
- Multiple sexual partners or unprotected sex
- History of other sexually transmitted infections
- Weakened immune system
- Young age at first sexual activity
- Partner with known HSV infection
Complications
- Recurrent painful outbreaks affecting quality of life
- Increased susceptibility to other STIs, including HIV
- Rarely, neonatal herpes if transmitted during childbirth
- Psychological stress or anxiety due to social stigma
Prevention
- Use condoms or dental dams during sexual activity
- Avoid sexual contact during active outbreaks
- Regular STI screening for sexually active individuals
- Open communication with partners about infection status
- Antiviral therapy to reduce viral shedding and transmission risk
Treatment Options in Korea
Treatment in Korea focuses on symptom management and reducing recurrence:
- Antiviral medications:
- Acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir for acute outbreaks or daily suppressive therapy
- Symptom relief:
- Pain management and topical care for sores
- Counseling and education:
- Guidance on preventing transmission and coping with social stigma
- Follow-up care:
- Regular monitoring to manage recurrent outbreaks and adjust treatment as needed
- Specialized hospitals:
- Dermatology and infectious disease departments at Samsung Medical Center, Seoul National University Hospital, and Asan Medical Center provide comprehensive care
With early diagnosis and proper antiviral therapy, patients in Korea can manage genital herpes effectively, minimize outbreaks, and reduce the risk of transmission.