Overview
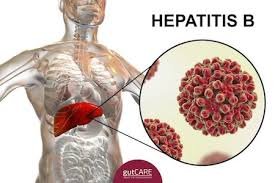
Hepatitis B is a viral infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). In Korea, hepatitis B has historically been prevalent, but widespread vaccination programs have significantly reduced new infections. Chronic hepatitis B remains a major public health concern due to its association with liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
What is Hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is a viral liver infection that can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-lasting). Chronic infection can lead to severe liver damage over time. The virus spreads through blood, sexual contact, or from mother to child during childbirth. People of all ages can be affected, though infants infected at birth are more likely to develop chronic infection.
Symptoms
- Fatigue and weakness
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal discomfort, especially in the upper right quadrant
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes)
- Dark urine and pale stools
- Fever or mild flu-like symptoms
Causes
- Infection with hepatitis B virus
- Mother-to-child transmission at birth
- Bloodborne exposure, such as shared needles or transfusions
- Sexual transmission through unprotected intercourse
Risk Factors
- Birth in or travel to areas with high HBV prevalence
- Infants born to HBV-infected mothers
- Unprotected sexual activity
- Intravenous drug use
- Healthcare workers exposed to blood or bodily fluids
- Family history of hepatitis B
Complications
Untreated or chronic hepatitis B can lead to:
- Liver cirrhosis
- Liver failure
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer)
- Chronic hepatitis with ongoing inflammation
- Increased risk of transmission to others
Prevention
- Universal vaccination at birth (widely implemented in Korea)
- Screening pregnant women to prevent mother-to-child transmission
- Safe sex practices and avoidance of sharing needles
- Regular monitoring for high-risk individuals
- Blood safety and sterilization protocols in medical settings
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea provides advanced care for hepatitis B, focusing on viral suppression and liver health:
- Medications:
- Antiviral therapies such as tenofovir or entecavir to control viral replication and prevent liver damage
- Monitoring:
- Regular liver function tests, HBV DNA testing, and imaging for cirrhosis or cancer
- Management of complications:
- Treatment for cirrhosis, variceal bleeding, or liver cancer as needed
- Liver transplantation:
- Available in severe cases at hospitals like Samsung Medical Center, Seoul National University Hospital, and Asan Medical Center
- Lifestyle guidance:
- Avoid alcohol, maintain a healthy diet, and monitor weight
- Public health measures:
- Vaccination campaigns, education, and screening programs
With early vaccination, monitoring, and antiviral therapy, patients in Korea can manage hepatitis B effectively, reducing the risk of severe liver disease and transmission.