Overview
Hepatic adenoma is a rare, benign liver tumor that can occasionally lead to complications such as bleeding or malignant transformation. In Korea, patients benefit from advanced diagnostic imaging, liver-focused medical care, and specialized surgical interventions in major hospitals.
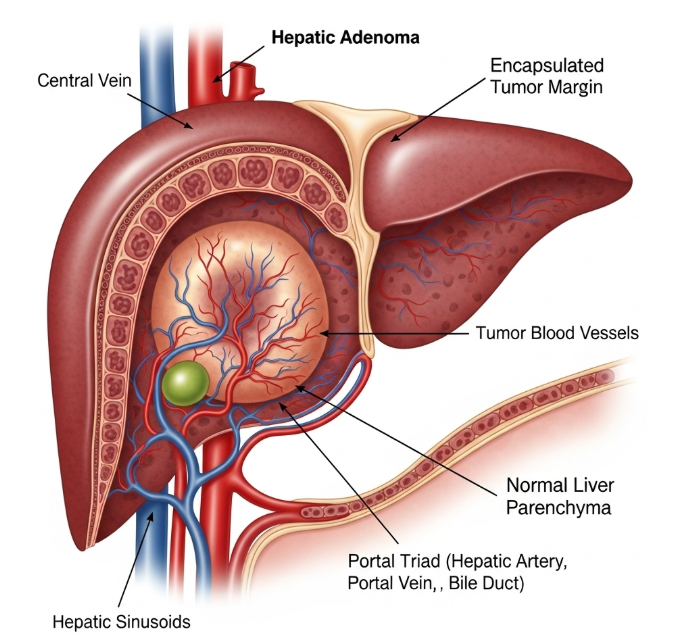
What is Hepatic Adenoma?
Hepatic adenoma is a non-cancerous liver lesion arising from hepatocytes. It most commonly affects women of childbearing age, particularly those using oral contraceptives, but can also appear in men or individuals with metabolic disorders.
Symptoms
- Often asymptomatic in early stages
- Abdominal pain or discomfort, usually in the right upper quadrant
- Nausea or vomiting
- Rarely, sudden severe abdominal pain if the tumor ruptures
- Possible palpable abdominal mass
- Signs of internal bleeding in case of rupture
Causes
- Hormonal factors, especially prolonged use of oral contraceptives or anabolic steroids
- Metabolic disorders such as glycogen storage diseases
- Obesity and fatty liver disease
- Genetic predispositions in rare cases
Risk Factors
- Female gender, particularly women aged 20–40
- Use of estrogen-containing medications
- Obesity and metabolic syndrome
- History of glycogen storage disorders
- Large hepatic adenomas (>5 cm)
Complications
- Tumor rupture causing internal bleeding (hemoperitoneum)
- Rare malignant transformation to hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pressure effects on surrounding organs
- Need for emergency surgery in case of hemorrhage
Prevention
- Limiting prolonged use of oral contraceptives when possible
- Maintaining healthy weight and managing metabolic disorders
- Regular medical check-ups for individuals at risk
- Imaging surveillance for known hepatic adenomas
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Ultrasound for initial detection of liver lesions
- CT scan or MRI for detailed assessment of size, location, and risk factors
- Blood tests to monitor liver function
- Biopsy in select cases to rule out malignancy
Medical & Surgical Treatments
- Observation for small, asymptomatic adenomas (<5 cm) with periodic imaging
- Surgical resection for large or symptomatic tumors
- Minimally invasive procedures such as laparoscopic hepatectomy in specialized centers
- Management of hormonal factors such as discontinuing oral contraceptives
- Emergency surgery in case of tumor rupture and bleeding
Rehabilitation and Support
- Post-surgical monitoring of liver function
- Lifestyle modifications to reduce metabolic risks
- Nutritional counseling to support liver health
- Regular imaging follow-up to detect recurrence or complications