Overview
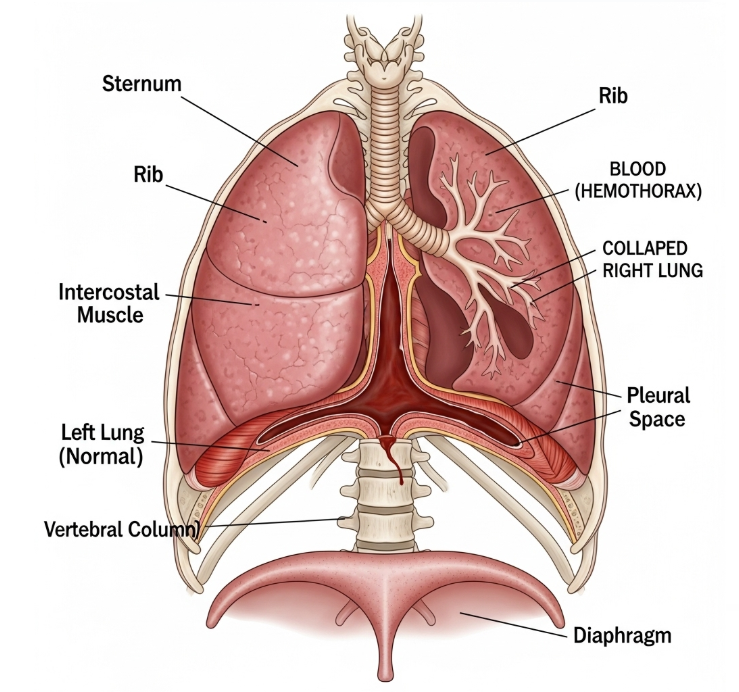
Hemothorax is a condition in which blood accumulates in the pleural cavity, the space between the lungs and chest wall. It can cause respiratory distress and reduced oxygenation. In Korea, emergency and thoracic surgery units provide advanced care for rapid diagnosis and treatment.
What is Hemothorax?
Hemothorax occurs when blood collects in the pleural space, often due to trauma, chest surgery, or underlying medical conditions such as blood clotting disorders. The accumulation of blood can compress the lung, reducing its ability to expand and impairing breathing.
Symptoms
- Chest pain, often sharp or sudden
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Rapid heart rate (tachycardia)
- Low blood pressure (hypotension)
- Cough, sometimes with blood
- Signs of shock in severe cases
Causes
- Blunt or penetrating chest trauma (accidents, falls, assaults)
- Complications after thoracic surgery or medical procedures
- Ruptured blood vessels in the chest
- Blood clotting disorders or anticoagulant therapy
- Spontaneous causes in certain lung diseases
Risk Factors
- Participation in contact sports or high-risk activities
- Pre-existing lung or heart conditions
- Use of blood-thinning medications
- Older age and frail health
- History of chest trauma or surgery
Complications
- Respiratory failure due to lung compression
- Hypovolemic shock from significant blood loss
- Infection in the pleural cavity (empyema)
- Long-term lung scarring or reduced function
- Recurrent hemothorax if underlying cause persists
Prevention
- Safety measures to prevent chest trauma
- Proper care during thoracic surgeries
- Monitoring and management of anticoagulant therapy
- Avoid high-risk activities when vulnerable
- Regular follow-up for patients with chronic lung or heart conditions
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Chest X-ray to detect fluid and blood in the pleural cavity
- CT scan for detailed imaging and assessment of bleeding source
- Blood tests to monitor hemoglobin, hematocrit, and coagulation
- Physical examination including vital signs and respiratory assessment
Medical & Surgical Treatments
- Chest tube insertion (thoracostomy) to drain blood and restore lung function
- Blood transfusions if significant bleeding occurs
- Surgery (thoracotomy or VATS) for ongoing bleeding or underlying injury
- Oxygen therapy and respiratory support
- Treatment of underlying causes such as trauma or clotting disorders
Rehabilitation and Support
- Pulmonary rehabilitation to restore lung capacity
- Gradual return to physical activity
- Follow-up imaging to ensure full recovery
- Patient education on preventing future injuries or complications