Overview
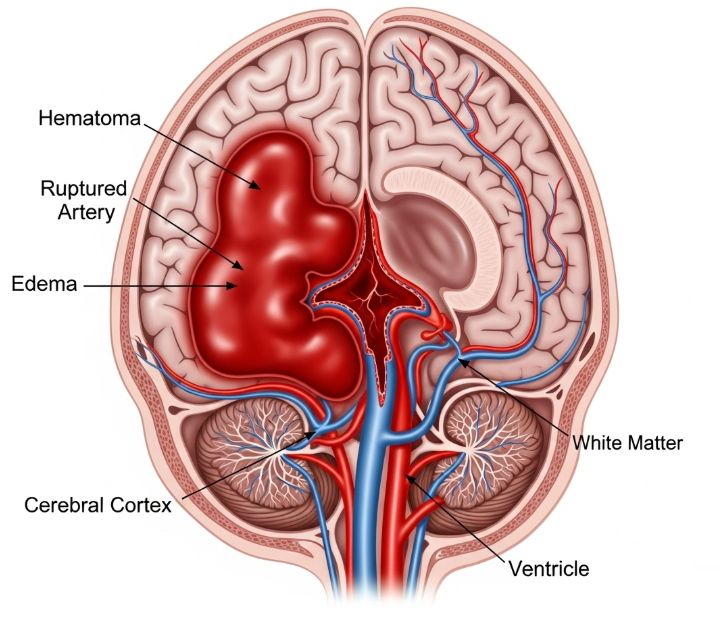
A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures, causing bleeding into brain tissue. It is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical intervention. In Korea, specialized stroke centers and neurosurgical departments provide rapid diagnosis and treatment to improve outcomes.
What is Hemorrhagic Stroke?
Hemorrhagic stroke is a type of stroke caused by intracerebral or subarachnoid bleeding, leading to increased intracranial pressure and brain damage. It can affect people of any age but is more common in older adults and those with uncontrolled hypertension or vascular abnormalities.
Symptoms
- Sudden severe headache
- Weakness or numbness on one side of the body
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Vision problems
- Loss of balance or coordination
- Nausea and vomiting
- Seizures
Causes
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Brain aneurysms or arteriovenous malformations
- Head trauma or injury
- Blood-thinning medications or clotting disorders
- Brain tumors or vascular malformations
Risk Factors
- Hypertension and cardiovascular disease
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Older age
- Family history of stroke
- Use of anticoagulant or antiplatelet medications
- Previous stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA)
Complications
- Permanent neurological deficits
- Paralysis or weakness
- Speech and cognitive impairments
- Seizures and brain swelling
- Increased risk of recurrent stroke
- Death in severe cases
Prevention
- Maintain healthy blood pressure and heart health
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake
- Regular physical activity and healthy diet
- Control diabetes and cholesterol levels
- Routine screening for aneurysms or vascular abnormalities in high-risk individuals
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- CT scan or MRI to locate and assess the extent of bleeding
- Cerebral angiography to detect vascular abnormalities
- Blood tests to evaluate coagulation and underlying conditions
- Neurological examination to assess brain function
Medical & Surgical Treatments
- Emergency stabilization including blood pressure management and supportive care
- Surgical interventions: Craniotomy, hematoma evacuation, or endovascular coiling for aneurysms
- Medications to control intracranial pressure, prevent seizures, and manage complications
- Rehabilitation therapies for motor, speech, and cognitive recovery
Rehabilitation and Support
- Physical therapy for mobility and strength recovery
- Occupational therapy to regain daily life skills
- Speech therapy for communication difficulties
- Psychological support for patients and families
- Long-term follow-up to monitor recovery and prevent recurrence