Overview
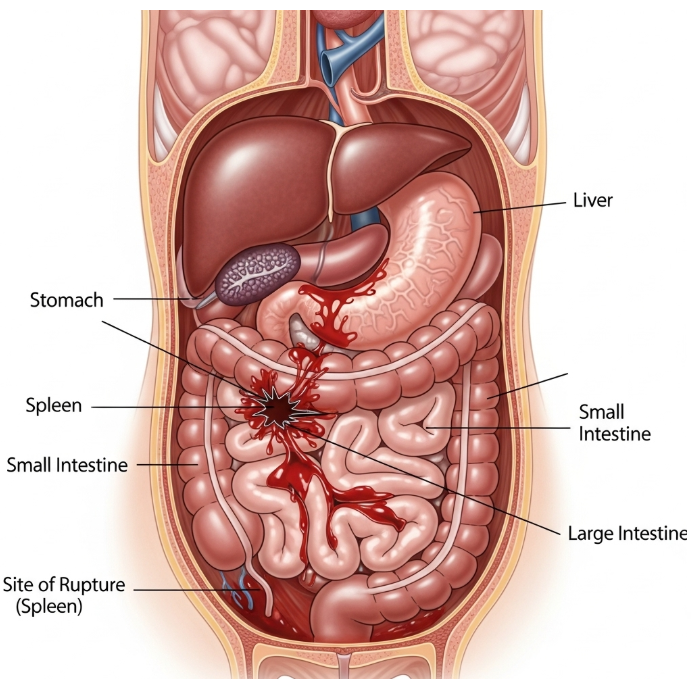
Hemoperitoneum is a medical emergency characterized by the accumulation of blood in the abdominal cavity. It is often caused by trauma, ruptured blood vessels, or abdominal organ injury. In Korea, prompt diagnosis and treatment at specialized trauma and surgical centers are essential to prevent life-threatening complications.
What is Hemoperitoneum?
Hemoperitoneum occurs when blood leaks into the peritoneal cavity, the space surrounding abdominal organs. It can develop rapidly due to injury or rupture of organs such as the spleen, liver, or major blood vessels, leading to hypovolemic shock if untreated.
Symptoms
- Severe abdominal pain or tenderness
- Abdominal swelling or distension
- Dizziness or fainting
- Rapid heart rate (tachycardia)
- Low blood pressure (hypotension)
- Signs of shock in severe cases
Causes
- Blunt or penetrating abdominal trauma (accidents, falls, assaults)
- Ruptured spleen or liver
- Ruptured abdominal aneurysm
- Complications during abdominal surgery
- Bleeding disorders or anticoagulant therapy
Risk Factors
- High-risk activities or contact sports
- Pre-existing aneurysms or liver disease
- Use of blood-thinning medications
- Trauma or recent abdominal surgery
- Age and underlying health conditions affecting clotting
Complications
- Hypovolemic shock and multi-organ failure
- Internal bleeding leading to death if untreated
- Infection or peritonitis
- Need for emergency surgery and intensive care
- Long-term abdominal or organ damage
Prevention
- Use protective gear in high-risk activities
- Manage underlying conditions such as aneurysms or liver disease
- Careful monitoring during and after surgery
- Avoidance of trauma-prone situations when possible
- Regular medical checkups for high-risk patients
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma (FAST) for rapid detection of internal bleeding
- CT scan of the abdomen to locate the source and extent of bleeding
- Blood tests to monitor hemoglobin, hematocrit, and coagulation
- Physical examination and vital signs monitoring
Medical & Surgical Treatments
- Emergency fluid resuscitation and blood transfusions
- Surgical intervention: Laparotomy or laparoscopic surgery to control bleeding
- Interventional radiology: Embolization of bleeding vessels in select cases
- Management of underlying causes (ruptured organ or vascular injury)
Rehabilitation and Support
- Intensive care monitoring post-surgery
- Gradual return to normal activity after stabilization
- Nutritional support for recovery
- Follow-up imaging to ensure no residual bleeding