Overview
Hemocholecystitis is a rare condition characterized by inflammation of the gallbladder accompanied by bleeding. It often results from gallstones, trauma, infection, or vascular disorders affecting the gallbladder. In Korea, advanced gastroenterology and hepatobiliary surgery centers provide comprehensive diagnosis and treatment options for this uncommon but potentially serious condition.
What is Hemocholecystitis?
Hemocholecystitis occurs when the gallbladder becomes inflamed and bleeding occurs within or around the organ. This can lead to abdominal pain, jaundice, or gastrointestinal bleeding. The condition may be acute or chronic, and in severe cases, it can cause gallbladder rupture or sepsis.
Symptoms
- Severe pain in the upper right abdomen
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever and chills
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin or eyes)
- Dark-colored urine or pale stools
- Abdominal tenderness
Causes
- Gallstones obstructing bile flow
- Trauma to the abdomen
- Vascular abnormalities or aneurysms in the gallbladder
- Bacterial infections leading to cholecystitis
- Coagulopathy or use of blood-thinning medications
Risk Factors
- Gallstone disease
- Chronic liver disease
- Anticoagulant therapy or blood clotting disorders
- Older age
- History of abdominal trauma or surgery
Complications
- Gallbladder rupture leading to peritonitis
- Sepsis and systemic infection
- Biliary obstruction causing jaundice
- Chronic gallbladder inflammation
- Internal bleeding with shock in severe cases
Prevention
- Managing gallstone risk through a healthy diet and regular checkups
- Avoiding abdominal trauma where possible
- Monitoring anticoagulant therapy carefully
- Regular liver function and abdominal imaging in high-risk individuals
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
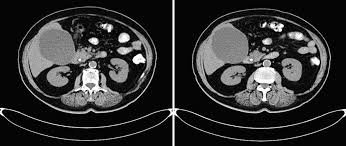
- Ultrasound to detect gallstones, bleeding, and gallbladder inflammation
- CT scan or MRI for detailed imaging of the gallbladder and surrounding organs
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) if bile duct obstruction is suspected
- Blood tests to assess liver function, infection, and coagulation
Medical & Surgical Treatments
- Hospitalization for acute cases with IV fluids, antibiotics, and pain management
- Surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy), performed laparoscopically or via open surgery
- Endoscopic or percutaneous drainage in high-risk patients
- Management of underlying bleeding disorders if present
Rehabilitation and Support
- Post-operative care and follow-up imaging
- Dietary counseling to prevent biliary complications
- Monitoring for signs of infection or bile leakage
- Pain management and gradual return to normal activities