Overview
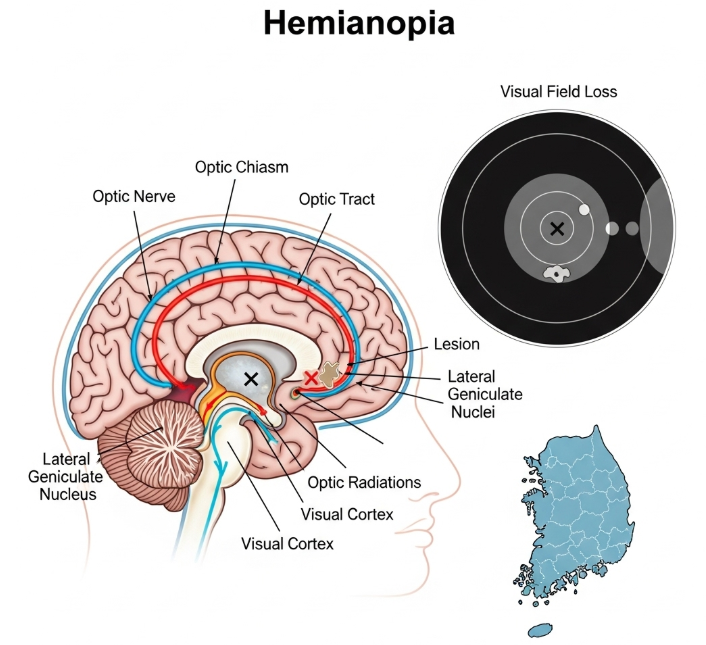
Hemianopia (also called hemianopsia) is a vision loss affecting half of the visual field in one or both eyes. It is not an eye disease itself but rather a neurological condition caused by damage to the brain’s visual pathways, often due to stroke, brain injury, or tumors. In Korea, with its advanced neurology, neurosurgery, and ophthalmology departments, hemianopia is carefully diagnosed and managed through a multidisciplinary approach.
What is Hemianopia?
Hemianopia occurs when the visual field is cut in half—either the left or right side (homonymous hemianopia), or the upper or lower half (quadrantanopia). This happens because the brain, rather than the eyes, processes vision. Damage to the optic nerve, optic tract, or occipital lobe often results in this condition. Patients may not notice the missing field at first but may experience difficulty with reading, driving, or navigating their environment.
Symptoms
- Loss of vision in half of the visual field (left, right, upper, or lower)
- Bumping into objects or people on one side
- Difficulty reading due to missing parts of text
- Poor depth perception
- Disorientation and visual confusion
- In some cases, visual hallucinations in the affected field
Causes
- Stroke (most common cause in Korea and worldwide)
- Traumatic brain injury
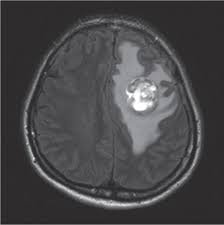
- Brain tumors affecting the occipital lobe or optic pathway
- Multiple sclerosis (damage to myelin affecting visual signals)
- Brain infections or inflammation
- Post-surgical complications from brain or eye surgery
Risk Factors
- Older age (higher risk of stroke and tumors)
- High blood pressure and cardiovascular disease
- Head injuries
- Brain surgery or radiation therapy
- Neurological disorders (like MS or epilepsy)
Complications
- Loss of independence (difficulty reading, driving, or walking safely)
- Increased risk of accidents or injuries
- Depression or anxiety due to vision impairment
- Reduced quality of life without rehabilitation
Prevention
While hemianopia itself cannot always be prevented, reducing risk factors for its causes is possible:
- Controlling blood pressure and cholesterol to prevent strokes
- Wearing helmets to avoid head injuries
- Managing chronic conditions like diabetes and heart disease
- Regular neurological checkups in Korea for patients with brain disorders
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Visual field testing (perimetry) to identify areas of vision loss
- MRI or CT scans to detect brain damage, tumors, or lesions
- Neurological exams to assess brain function
- Ophthalmologic evaluation for related eye health
Medical & Surgical Treatments
- Stroke management (antiplatelet therapy, anticoagulants, and rehabilitation)
- Surgery or radiation therapy for brain tumors
- Steroids or immunotherapy for inflammatory conditions like MS
- Vision therapy and rehabilitation using specialized exercises and adaptive strategies
Rehabilitation and Support
- Visual scanning training to help patients learn to scan into the blind field
- Prism glasses to expand visual field
- Occupational therapy for mobility and reading adaptations
- Assistive technology (screen readers, magnifiers, special software)
- Multidisciplinary rehab centers in Korea help patients regain independence