Overview
Helminth infections are caused by parasitic worms such as roundworms, flatworms, and flukes that live inside the human body, usually in the intestines. These infections were once common in Korea due to agricultural practices, but with improved sanitation and nationwide deworming programs, the prevalence has decreased significantly. Today, helminth infections in Korea are relatively rare, but they can still occur due to imported cases, contaminated food, or travel-related exposure.
What is Helminth Infection?
Helminths are parasitic worms that infect humans, causing a range of gastrointestinal and systemic problems. They include:
- Nematodes (roundworms) – e.g., Ascaris, hookworms
- Cestodes (tapeworms) – e.g., Taenia species
- Trematodes (flukes) – e.g., liver flukes, blood flukes
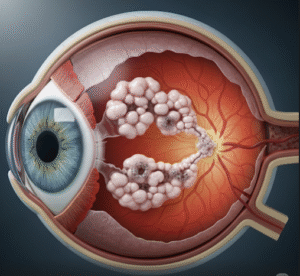
In Korea, infections with liver flukes (Clonorchis sinensis) have been of particular concern due to the habit of eating raw freshwater fish.
Symptoms
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Bloating and nausea
- Fatigue and weakness
- Weight loss or malnutrition
- Itchy skin or rashes (in some worm infections)
- Anemia (from hookworms or heavy infestations)
Causes
- Consuming contaminated food or water
- Eating raw or undercooked freshwater fish (leading to liver fluke infection)
- Poor sanitation or hygiene
- Walking barefoot on contaminated soil (hookworms)
- Travel to areas where helminth infections are still common
Risk Factors
- Eating raw freshwater fish (a cultural practice in some rural Korean regions)
- Living near rivers and agricultural lands
- Traveling to endemic countries
- Weakened immune system
- Lack of regular deworming
Complications
- Severe malnutrition and stunted growth in children
- Chronic anemia
- Intestinal obstruction (in heavy roundworm infestations)
- Liver or bile duct damage from liver flukes
- Increased risk of cholangiocarcinoma (bile duct cancer) with chronic liver fluke infection
Prevention
- Avoid eating raw or undercooked freshwater fish
- Practice good hygiene and sanitation
- Use safe drinking water sources
- Wear protective footwear when outdoors
- Participate in regular health screenings if at risk
- Public health education on food safety
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Stool tests for parasite eggs or larvae
- Blood tests for antibodies
- Imaging (ultrasound, CT, or MRI) in cases of liver fluke infection
- Endoscopic evaluation for complications
Medical Treatments
- Antiparasitic medications such as albendazole, mebendazole, or praziquantel
- Nutritional support to manage malnutrition or anemia
- Iron and vitamin supplementation when needed
- Regular follow-up stool exams to ensure eradication
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Endoscopic or surgical removal in rare cases of intestinal blockage
- Advanced hepatology treatments for liver damage due to chronic fluke infection
Rehabilitation and Support
- Nutritional counseling for recovery from malnutrition
- Long-term follow-up for patients with liver fluke complications
- Preventive education to avoid re-infection