Overview
Heart block is a condition in which the electrical signals that control the heartbeat are partially or completely blocked, leading to an abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia). It can range from mild and asymptomatic to severe, requiring medical intervention.
In Korea, heart block is diagnosed and treated in cardiology and electrophysiology centers, where advanced monitoring and pacemaker therapies are widely available.
What is Heart Block?
Heart block occurs when electrical impulses traveling from the atria to the ventricles are delayed or blocked. It is classified into first-degree, second-degree, and third-degree (complete) heart block, with increasing severity. The condition can affect people of any age, including newborns (congenital heart block) and older adults.
Symptoms
- Slow or irregular heartbeat
- Fatigue or weakness
- Dizziness or fainting (syncope)
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Palpitations
- In infants: poor feeding or lethargy
Causes
- Age-related degeneration of the heart’s conduction system
- Heart disease, including myocardial infarction or cardiomyopathy
- Inflammatory or autoimmune diseases
- Congenital heart defects
- Certain medications (beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, antiarrhythmic drugs)
- Electrolyte imbalances
Risk Factors
- Older age
- Heart disease history
- High blood pressure
- Congenital heart conditions
- Previous heart surgery or heart attack
- Family history of arrhythmias
Complications
- Severe bradycardia leading to fainting or dizziness
- Heart failure due to inefficient pumping
- Sudden cardiac arrest in complete heart block
- Need for long-term pacemaker implantation
- Reduced quality of life due to fatigue and activity limitation
Prevention
- Regular cardiac check-ups, especially for high-risk individuals
- Management of underlying heart disease and risk factors
- Careful use of medications affecting heart rhythm
- Healthy lifestyle, including balanced diet, exercise, and blood pressure control
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) to detect abnormal heart rhythms
- Holter monitoring for continuous rhythm assessment
- Electrophysiological studies for detailed conduction analysis
- Echocardiography to evaluate heart structure and function
Medical Treatments
- Observation for mild, asymptomatic cases
- Adjustment of medications contributing to heart block
- Treatment of underlying heart disease or electrolyte imbalances
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
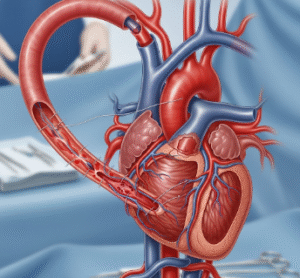
- Pacemaker implantation for symptomatic or severe heart block
- Advanced cardiac monitoring devices available in major Korean hospitals
- Minimally invasive pacemaker insertion with short recovery times
Rehabilitation and Support
- Regular follow-up and pacemaker checks
- Lifestyle guidance to prevent further heart disease
- Cardiac rehabilitation programs for improved physical fitness
- Patient education on recognizing warning signs and device management