Overview
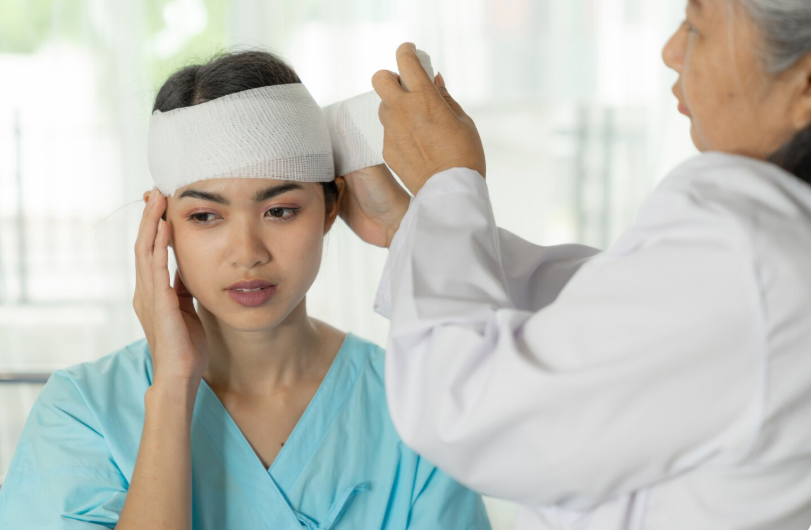
Head trauma refers to any injury to the scalp, skull, or brain, ranging from minor bumps to severe traumatic brain injury (TBI). It is a significant health concern due to its potential for long-term neurological complications.
In Korea, head trauma is treated in emergency departments, neurosurgery units, and rehabilitation centers, with an emphasis on rapid diagnosis, acute care, and neurorehabilitation to minimize long-term damage.
What is Head Trauma?
Head trauma occurs when an external force impacts the head, potentially causing skull fractures, brain contusions, bleeding, or diffuse axonal injury. It affects individuals of all ages, with higher incidence in traffic accidents, falls, and sports injuries.
Symptoms
- Loss of consciousness or confusion
- Headache and dizziness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Blurred vision or sensitivity to light
- Weakness or numbness in limbs
- Seizures
- Memory or concentration problems
Causes
- Road traffic accidents
- Falls from height
- Sports-related injuries
- Physical assaults or violence
- Industrial or workplace accidents
Risk Factors
- Young adults and elderly individuals
- Participation in high-risk sports or activities
- Alcohol or substance use
- Lack of protective headgear
- Previous head injury
Complications
- Traumatic brain injury (TBI)
- Intracranial hemorrhage (epidural, subdural, intracerebral)
- Skull fractures
- Cognitive or memory impairments
- Seizures or post-traumatic epilepsy
- Long-term disability or neurological deficits
Prevention
- Wear helmets for cycling, motorcycling, or contact sports
- Implement fall-prevention measures at home and workplaces
- Use seat belts in vehicles
- Avoid risky behavior under the influence of alcohol
- Ensure proper safety equipment in sports and industrial environments
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Physical and neurological examination
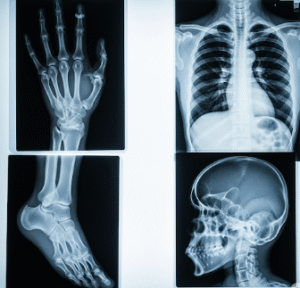
- CT scans and MRI to detect fractures, bleeding, or brain swelling
- Skull X-rays for minor injuries
- Monitoring intracranial pressure in severe cases
Medical Treatments
- Rest and observation for mild concussions
- Medications for pain, swelling, or seizures
- Intravenous fluids and supportive care in hospitalized patients
- Close monitoring in emergency departments for early intervention
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Craniotomy or craniectomy for intracranial hemorrhage
- Endoscopic or minimally invasive surgery for skull fractures or hematomas
- ICP (intracranial pressure) management in severe brain injuries
- Korean trauma centers provide advanced neurosurgical and critical care services
Rehabilitation and Support
- Physical, occupational, and speech therapy
- Cognitive rehabilitation for memory, attention, and executive function
- Psychological counseling for emotional and behavioral changes
- Long-term follow-up to assess recovery and prevent complications