Overview
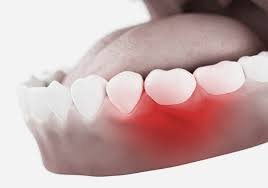
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an infection of the tissues surrounding the teeth, primarily caused by bacterial plaque buildup. It ranges from mild gingivitis to advanced periodontitis, which can lead to tooth loss if untreated. In Korea, dental care is widely accessible, and modern clinics offer advanced preventive, diagnostic, and treatment options for gum disease.
Symptoms
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding during brushing or flossing
- Persistent bad breath
- Receding gums or longer-looking teeth
- Formation of deep pockets between teeth and gums
- Loose or shifting teeth in severe cases
Causes
Gum disease is primarily caused by the accumulation of bacterial plaque on teeth and gums. Contributing factors include:
- Poor oral hygiene
- Smoking or tobacco use
- Hormonal changes (puberty, pregnancy, menopause)
- Certain medications that reduce saliva flow
- Chronic illnesses (diabetes, immune disorders)
- Genetic susceptibility
Risk Factors
- Inadequate oral hygiene
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Poor diet or vitamin deficiencies
- Diabetes and other chronic diseases
- Family history of periodontal disease
- Stress or immune system disorders
Diagnosis
In Korea, gum disease is diagnosed using:
- Dental examination to check for plaque, tartar, and gum inflammation
- Periodontal probing to measure pocket depths around teeth
- Dental X-rays to detect bone loss
- Medical history review to identify contributing conditions
Prevention
- Brushing teeth at least twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
- Daily flossing to remove plaque between teeth
- Regular dental check-ups and professional cleaning
- Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol
- Maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean dental clinics provide comprehensive care for gum disease:
- Non-Surgical Treatment
- Professional dental cleaning (scaling and root planing)
- Improved oral hygiene instruction
- Antimicrobial mouth rinses
- Surgical Treatment
- Flap surgery to reduce pocket depth
- Bone grafts or tissue regeneration for severe cases
- Laser therapy for targeted removal of diseased tissue
- Maintenance and Follow-Up
- Regular check-ups and cleanings every 3–6 months
- Monitoring of oral hygiene and periodontal health
- Patient education on lifestyle modifications
Prognosis
With early detection and proper care, gum disease can be effectively managed, and tooth loss can be prevented. In Korea, access to advanced dental care ensures high success rates, though untreated or severe cases can lead to permanent gum and bone damage, tooth loss, and increased risk of systemic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes.