Overview
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD), also known as acid reflux, occurs when stomach acid or contents flow back into the oesophagus, causing irritation and discomfort. While occasional reflux is common, persistent symptoms can lead to complications. In Korea, advanced diagnostic tools and effective treatment options are widely available for managing GORD.
What is GORD (reflux)?
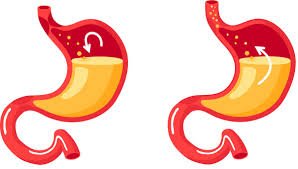
GORD is a chronic digestive disorder where the lower oesophageal sphincter (LES) — the valve between the oesophagus and stomach — does not function properly, allowing stomach acid to escape into the oesophagus. This backflow causes symptoms like heartburn, regurgitation, and sometimes chest pain.
Symptoms
- Persistent heartburn, especially after meals
- Acid regurgitation
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Chronic cough or sore throat
- Chest discomfort or burning sensation
- Hoarseness or voice changes
Causes
- Weak or relaxed lower oesophageal sphincter
- Hiatal hernia
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Certain foods and drinks (spicy food, caffeine, alcohol)
- Smoking
- Certain medications (e.g., NSAIDs, calcium channel blockers)
Risk Factors
- Being overweight or obese
- Smoking
- Eating large meals or lying down soon after eating
- High-fat or spicy diet
- Chronic stress
- Family history of reflux disease
Complications
- Oesophagitis (inflammation of the oesophagus)
- Oesophageal stricture (narrowing)
- Barrett’s oesophagus (precancerous changes)
- Oesophageal cancer
- Chronic respiratory issues (asthma, bronchitis)
Prevention
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals
- Avoid lying down within 2–3 hours after eating
- Limit alcohol, caffeine, and acidic or spicy foods
- Quit smoking
- Elevate the head of the bed when sleeping
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers comprehensive GORD care using both non-surgical and surgical methods:
- Diagnosis: Endoscopy, 24-hour pH monitoring, oesophageal manometry
- Medication: Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), H2 receptor blockers, antacids
- Lifestyle programs: Diet counselling, weight management, smoking cessation
- Surgical options: Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication, LINX reflux management system for severe cases
- Advanced care: Minimally invasive techniques and long-term monitoring for complications like Barrett’s oesophagus