Overview
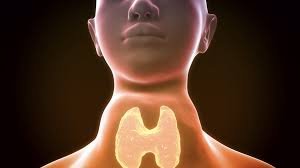
Goitre is the abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland, located in the neck. In South Korea, goitre can result from iodine deficiency, autoimmune thyroid disorders, or other thyroid-related conditions. While some goitres are harmless, others may cause symptoms or indicate underlying thyroid dysfunction.
Symptoms
- Visible swelling in the neck
- Tightness or pressure in the throat
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing (in large goitres)
- Hoarseness or voice changes
- Symptoms of thyroid dysfunction, such as fatigue, weight changes, or palpitations
Some goitres may not produce noticeable symptoms and are discovered during routine medical examinations.
Prevention
- Maintain sufficient iodine intake through diet
- Regular medical check-ups for thyroid function
- Early evaluation of neck swelling or thyroid-related symptoms
- Awareness of family history and personal risk factors
Causes
- Iodine deficiency in the diet
- Autoimmune thyroid diseases, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or Graves’ disease
- Nodules or cysts in the thyroid
- Inflammation of the thyroid (thyroiditis)
- Certain medications affecting thyroid function
- Genetic predisposition
Risk Factors
- Living in areas with low dietary iodine intake
- Female gender (more commonly affected than males)
- Age, particularly middle-aged and older adults
- Family history of thyroid disorders
- Existing autoimmune conditions
Diagnosis
- Physical examination to assess thyroid size and consistency
- Blood tests to measure thyroid hormones (TSH, T3, T4)
- Ultrasound of the thyroid to detect nodules or cysts
- Fine-needle aspiration biopsy for suspicious nodules
- Iodine level assessment if deficiency is suspected
Treatment Options in Korea
- Medical Management:
- Iodine supplementation for deficiency-related goitre
- Medications to treat hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism
- Surgical Intervention:
- Thyroidectomy may be performed for large goitres causing symptoms or if malignancy is suspected
- Regular Monitoring:
- Periodic thyroid function tests and ultrasound evaluations to track changes
- Lifestyle and Dietary Advice:
- Adequate dietary iodine intake through iodized salt, seafood, and dairy products
- Monitoring for triggers or factors affecting thyroid health
Prognosis
The outlook for individuals with goitre in Korea depends on the underlying cause. Iodine deficiency-related goitres usually respond well to supplementation. Autoimmune or nodular goitres may require ongoing management, but most cases are manageable with proper care and monitoring.