Overview
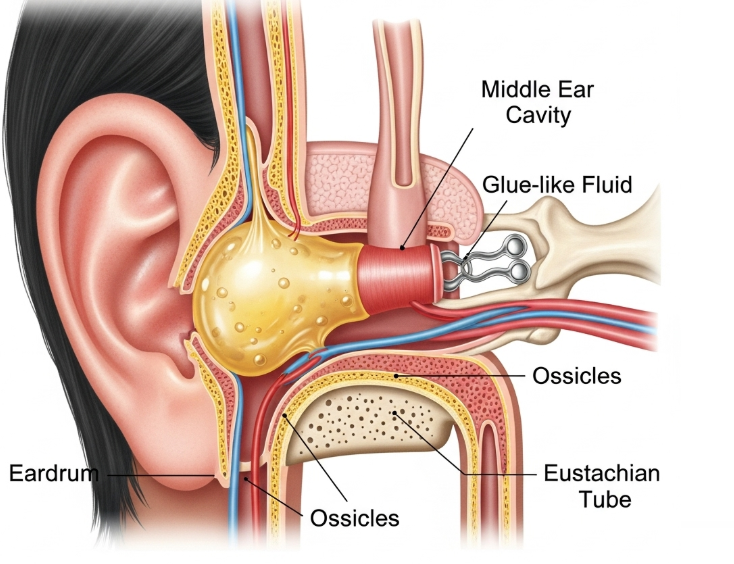
Glue ear, medically known as otitis media with effusion (OME), is a condition where the middle ear fills with thick, sticky fluid instead of air. It is common in children but can also affect adults. While not usually painful, it can cause hearing difficulties and affect speech, language, and learning in children. Korea provides specialized ENT (ear, nose, and throat) clinics with advanced diagnostics and treatment options for glue ear.
What is Glue Ear?
Glue ear occurs when fluid accumulates behind the eardrum, often due to Eustachian tube dysfunction, allergies, or infections. The fluid impairs sound conduction, leading to hearing problems. Chronic cases can affect speech development and balance in children.
Symptoms
- Mild hearing loss or difficulty hearing soft sounds
- Feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear
- Balance problems or clumsiness
- Delayed speech or language development in children
- Occasional ear discomfort or popping sounds
- Irritability or attention difficulties in children
Causes
- Blockage or dysfunction of the Eustachian tube
- Upper respiratory infections or frequent colds
- Allergies affecting the nasal passages and sinuses
- Enlarged adenoids or tonsils
- Exposure to smoke or environmental irritants
Risk Factors
- Age 6 months to 3 years (most common in children)
- Frequent colds or sinus infections
- Family history of glue ear or chronic ear problems
- Attending daycare (increased exposure to infections)
- Allergies or asthma
- Exposure to secondhand smoke
Complications
- Persistent hearing loss affecting speech, language, and learning
- Recurrent ear infections
- Delayed social or cognitive development in children
- Chronic middle ear fluid leading to tympanic membrane damage
Prevention
- Treat and manage upper respiratory infections promptly
- Reduce exposure to secondhand smoke
- Practice good hand hygiene to prevent infections
- Manage allergies effectively
- Encourage proper feeding positions in infants to prevent fluid accumulation
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers modern ENT care for glue ear, including both conservative and surgical approaches:
- Diagnosis
- Otoscopy and pneumatic otoscopy to visualize fluid
- Tympanometry to assess middle ear pressure
- Hearing tests for children to evaluate hearing impact
- Conservative Management
- Watchful waiting (fluid may resolve on its own)
- Nasal decongestants or saline sprays for temporary relief
- Allergy management if relevant
- Surgical Intervention
- Grommet (tympanostomy) insertion: Small tubes placed in the eardrum to drain fluid and ventilate the middle ear
- Adenoidectomy: Removal of enlarged adenoids if contributing to Eustachian tube blockage
- Follow-up Care
- Regular hearing checks to monitor recovery
- Speech therapy if hearing loss affected speech development
- Management of recurrent infections