Overview
Pediatric gliomas are a group of brain tumors originating from glial cells in the central nervous system. These tumors are the most common type of brain cancer in children. In South Korea, advancements in medical research and healthcare infrastructure have significantly improved the diagnosis, treatment, and survival rates for children affected by gliomas.
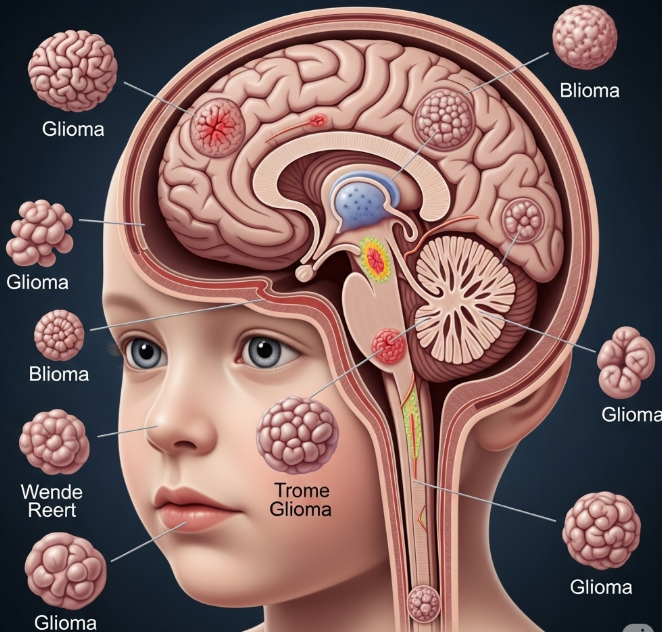
What are Pediatric Gliomas?
Pediatric gliomas encompass a variety of tumors, including:
- Low-Grade Gliomas (LGGs): Typically slow-growing and often benign. The most common subtype is pilocytic astrocytoma, which accounts for approximately 30% of pediatric brain tumors .
- High-Grade Gliomas (HGGs): More aggressive and malignant tumors. These include diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG), a particularly challenging form due to its location and prognosis .
Symptoms
The symptoms of pediatric gliomas vary depending on the tumor’s location and size but may include:
- Persistent headaches
- Nausea and vomiting
- Seizures
- Vision problems
- Balance and coordination issues
- Behavioral or cognitive changes
Causes
The exact cause of pediatric gliomas is not fully understood. However, factors that may contribute include:
- Genetic mutations
- Family history of brain tumors
- Environmental exposures
Risk Factors
Certain factors may increase the risk of developing pediatric gliomas:
- Age: Most common in children aged 5–14 years
- Gender: Slightly more prevalent in males
- Genetic conditions such as neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1)
Complications
If left untreated or inadequately managed, pediatric gliomas can lead to:
- Neurological deficits
- Hormonal imbalances
- Cognitive impairments
- Reduced quality of life
Prevention
While there is no known way to prevent pediatric gliomas, early detection and treatment are crucial. Regular neurological check-ups and awareness of symptoms can aid in prompt diagnosis.
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers state-of-the-art medical care for pediatric gliomas, with leading hospitals providing comprehensive treatment options:
- Diagnosis:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Computed Tomography (CT) scans
- Biopsy procedures
- Treatment Modalities:
- Surgical Intervention: Removal of the tumor when feasible, especially for LGGs.
- Radiation Therapy: Often used for HGGs and DIPG, though its application is carefully considered in children due to potential long-term effects.
- Chemotherapy: Utilized for tumors that cannot be surgically removed or are at high risk of recurrence.
- Targeted Therapies: Emerging treatments focusing on specific genetic mutations within the tumor cells.
- Clinical Trials: Participation in ongoing research studies may provide access to new therapies and contribute to advancing medical knowledge.
- Rehabilitation Services: Post-treatment support, including physical, occupational, and speech therapy, to aid in recovery and improve quality of life.