Overview
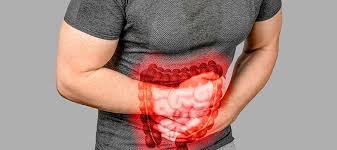
Gastrointestinal illnesses refer to a broad range of conditions affecting the digestive tract, which includes the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas. These disorders can range from mild, temporary discomforts like indigestion to serious, chronic diseases such as Crohn’s disease or gastrointestinal cancers. Symptoms may vary significantly depending on the condition but often involve abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation.
South Korea is known for its advanced medical technology, highly trained gastroenterologists, and state-of-the-art diagnostic facilities. Patients in Korea have access to world-class hospitals and clinics that specialize in gastrointestinal disorders, offering both rapid diagnosis and a wide range of treatment options.
What is Gastrointestinal Illness?
Gastrointestinal illness is an umbrella term for diseases and disorders affecting the digestive system. These may be caused by infections, inflammation, structural abnormalities, autoimmune reactions, metabolic disorders, or cancer. The gastrointestinal system plays a vital role in breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste, so any disruption can have a major impact on overall health.
Gastrointestinal illnesses can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-lasting). Acute conditions, such as gastroenteritis or food poisoning, often resolve within days or weeks, while chronic conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), may require lifelong management.
Symptoms
Symptoms of gastrointestinal illnesses vary depending on the specific condition but may include:
- Abdominal pain or cramps
- Bloating and excessive gas
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea (acute or chronic)
- Constipation
- Loss of appetite
- Heartburn or acid reflux
- Unexplained weight loss
- Blood in stool or black, tarry stools
- Fatigue related to malnutrition or chronic illness
Causes
The causes of gastrointestinal illnesses are diverse and may include:
- Infections: Viruses (norovirus, rotavirus), bacteria (Salmonella, E. coli, H. pylori), or parasites (Giardia, Entamoeba).
- Inflammatory conditions: Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, gastritis.
- Functional disorders: Irritable bowel syndrome, functional dyspepsia.
- Structural abnormalities: Hernias, strictures, diverticulosis.
- Dietary factors: High-fat, low-fiber diets, excessive alcohol consumption, food intolerances.
- Autoimmune reactions: Celiac disease, autoimmune hepatitis.
- Cancers: Stomach cancer, colorectal cancer, pancreatic cancer.
- Medications: NSAIDs, antibiotics, or chemotherapy drugs affecting the digestive tract.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing gastrointestinal illnesses:
- Poor dietary habits (low fiber, high processed food intake)
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Smoking
- Chronic stress
- Family history of GI diseases
- Advanced age (risk increases with age)
- Frequent travel to regions with poor sanitation
- Weakened immune system due to illness or medications
- Sedentary lifestyle
Complications
If left untreated, gastrointestinal illnesses can lead to serious complications, including:
- Severe dehydration and electrolyte imbalances
- Chronic malnutrition and weight loss
- Intestinal perforation
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
- Organ damage (liver, pancreas)
- Increased risk of colorectal cancer
- Strictures and bowel obstruction
- Sepsis in severe infection cases
Prevention
While not all gastrointestinal illnesses can be prevented, the following measures significantly reduce the risk:
- Maintaining a healthy, balanced diet rich in fiber, fruits, and vegetables
- Drinking safe, clean water
- Practicing proper food hygiene and cooking meats thoroughly
- Regular handwashing with soap and water
- Avoiding excessive alcohol and caffeine
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques
- Avoiding unnecessary use of NSAIDs and antibiotics
- Regular health checkups and colonoscopy screenings as recommended
- Receiving vaccinations such as hepatitis A and rotavirus (for children)
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea’s healthcare system offers a comprehensive approach to diagnosing and treating gastrointestinal illnesses, combining modern technology with expert medical care.
Diagnosis
- Medical history and physical examination
- Endoscopy (upper GI endoscopy, colonoscopy)
- Imaging scans (CT, MRI, ultrasound)
- Stool tests for bacteria, viruses, and parasites
- Blood tests to check for infection, inflammation, or nutritional deficiencies
- Breath tests for H. pylori detection
- Biopsies for suspected cancers or chronic inflammation
Medical Treatments
- Medications:
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections
- Antiparasitic drugs for parasitic infestations
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or H2 blockers for acid-related conditions
- Anti-inflammatory medications for IBD
- Antispasmodics for IBS symptoms
- Antiemetics for nausea and vomiting
- Intravenous (IV) fluids for dehydration
- Nutritional therapy for malnutrition or food intolerances
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery for hernias, gallbladder removal, or bowel resections
- Endoscopic removal of polyps or small tumors
- Surgery for severe IBD or bowel obstructions
- Liver transplants for end-stage liver disease
- Advanced cancer treatments including targeted therapy and immunotherapy
Rehabilitation and Support
- Dietary counseling with nutritionists
- Stress management programs for functional GI disorders
- Support groups for patients with chronic conditions
- Long-term follow-up care to monitor and prevent relapse