Overview
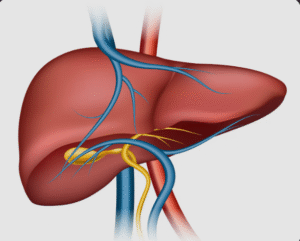
Gallstones are hardened deposits of digestive fluid (bile) that form in the gallbladder — a small organ under the liver that stores bile. They can range in size from tiny grains to several centimeters in diameter. While some gallstones cause no symptoms, others can lead to sudden, intense pain and potentially serious complications.
What is Gallstones?
Gallstones, medically known as cholelithiasis, develop when there is an imbalance in the substances that make up bile — such as cholesterol, bile salts, and bilirubin. They can block the flow of bile through the bile ducts, leading to pain, inflammation, or infection.
Symptoms
- Sudden, intense pain in the upper right or middle abdomen (gallbladder attack)
- Pain between the shoulder blades or in the right shoulder
- Nausea or vomiting
- Indigestion, bloating, or discomfort after fatty meals
- Fever and jaundice (if infection or blockage occurs)
Causes
- Excess cholesterol in bile
- Excess bilirubin in bile
- Incomplete emptying of the gallbladder
- Rapid weight loss or prolonged fasting
Risk Factors
- Female gender
- Age over 40
- Obesity or rapid weight loss
- Pregnancy
- High-fat, high-cholesterol, low-fiber diet
- Family history of gallstones
- Certain medical conditions (e.g., liver disease, diabetes)
Complications
- Gallbladder inflammation (cholecystitis)
- Blockage of bile ducts (choledocholithiasis)
- Pancreatitis (if the stone blocks the pancreatic duct)
- Gallbladder infection or rupture
- Jaundice
Prevention
- Maintain a healthy weight and avoid rapid weight loss
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fiber and low in saturated fat
- Exercise regularly
- Stay hydrated
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers advanced and patient-friendly treatments for gallstones, often using minimally invasive techniques:
- Watchful Waiting – If gallstones cause no symptoms, monitoring may be recommended.
- Medication – Certain oral bile acid pills can dissolve cholesterol gallstones (effective only in select cases).
- Non-Surgical Stone Removal – Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) to remove stones in bile ducts.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery – Laparoscopic cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder) is the most common and highly successful treatment in Korean hospitals, allowing fast recovery (often within 1 week).
- Single-Incision or Robotic Surgery – Offered in advanced Korean centers for smaller scars and quicker healing.